24(S)-Hydroxycholesterol as a Modulator of Neuronal Signaling and Survival
- PMID: 25628343
- PMCID: PMC4821654
- DOI: 10.1177/1073858414568122
24(S)-Hydroxycholesterol as a Modulator of Neuronal Signaling and Survival
Abstract
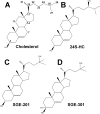
The major cholesterol metabolite in brain, 24(S)-hydroxycholesterol (24S-HC), serves as a vehicle for cholesterol removal. Its effects on neuronal function, however, have only recently begun to be investigated. Here, we review that nascent work. Our own studies have demonstrated that 24S-HC has potent positive modulatory effects on N-methyl-d-aspartate (NMDA) receptor (NMDAR) function. This could have implications not only for brain plasticity but also for pathological NMDAR overuse. Other work has demonstrated effects of 24S-HC on neuronal survival and as a possible biomarker of neurodegenerative disease. Depending on circumstances, both upregulation/mimicry of 24S-HC signaling and down-regulation/antagonism may have therapeutic potential. We are interested in the possibility that synthetic analogues of 24S-HC with positive effects at NMDARs may hold neurotherapeutic promise, given the role of NMDA receptor hypofunction in certain neuropsychiatric disorders.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; NMDA; apoptosis; cholesterol. 24(S)-hydroxycholesterol; glutamate.
© The Author(s) 2015.
Figures



References
-
- Abildayeva K, Jansen PJ, Hirsch-Reinshagen V, Bloks VW, Bakker AH, Ramaekers FC, et al. 24(S)-hydroxycholesterol participates in a liver X receptor-controlled pathway in astrocytes that regulates apolipoprotein E-mediated cholesterol efflux. J Biol Chem. 2006;281(18):12799–808. - PubMed
-
- Allen JA, Halverson-Tamboli RA, Rasenick MM. Lipid raft microdomains and neurotransmitter signalling. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2007;8(2):128–40. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

