Accurate transcriptome-wide prediction of microRNA targets and small interfering RNA off-targets with MIRZA-G
- PMID: 25628353
- PMCID: PMC4330396
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkv050
Accurate transcriptome-wide prediction of microRNA targets and small interfering RNA off-targets with MIRZA-G
Erratum in
-
Accurate transcriptome-wide prediction of microRNA targets and small interfering RNA off-targets with MIRZA-G.Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 15;43(18):9095. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkv924. Epub 2015 Sep 13. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015. PMID: 26365243 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
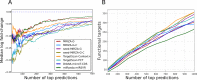
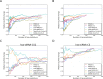
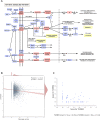
Small interfering RNA (siRNA)-mediated knock-down is a widely used experimental approach to characterizing gene function. Although siRNAs are designed to guide the cleavage of perfectly complementary mRNA targets, acting similarly to microRNAs (miRNAs), siRNAs down-regulate the expression of hundreds of genes to which they have only partial complementarity. Prediction of these siRNA 'off-targets' remains difficult, due to the incomplete understanding of siRNA/miRNA-target interactions. Combining a biophysical model of miRNA-target interaction with structure and sequence features of putative target sites we developed a suite of algorithms, MIRZA-G, for the prediction of miRNA targets and siRNA off-targets on a genome-wide scale. The MIRZA-G variant that uses evolutionary conservation performs better than currently available methods in predicting canonical miRNA target sites and in addition, it predicts non-canonical miRNA target sites with similarly high accuracy. Furthermore, MIRZA-G variants predict siRNA off-target sites with an accuracy unmatched by currently available programs. Thus, MIRZA-G may prove instrumental in the analysis of data resulting from large-scale siRNA screens.
© The Author(s) 2015. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Figures
References
-
- Huntzinger E., Izaurralde E. Gene silencing by microRNAs: contributions of translational repression and mRNA decay. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2011;12:99–110. - PubMed
-
- Calin G.A., Croce C.M. MicroRNA signatures in human cancers. Nat. Rev. Cancer. 2006;6:857–866. - PubMed
-
- Rajewsky N., Socci N.D. Computational identification of microRNA targets. Dev. Biol. 2004;267:529–535. - PubMed
-
- Lewis B.P., Burge C.B., Bartel D.P. Conserved seed pairing, often flanked by adenosines, indicates that thousands of human genes are microRNA targets. Cell. 2005;120:15–20. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

