Molecular mechanisms of acrolein toxicity: relevance to human disease
- PMID: 25628402
- PMCID: PMC4306719
- DOI: 10.1093/toxsci/kfu233
Molecular mechanisms of acrolein toxicity: relevance to human disease
Abstract
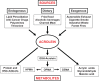
Acrolein, a highly reactive unsaturated aldehyde, is a ubiquitous environmental pollutant and its potential as a serious environmental health threat is beginning to be recognized. Humans are exposed to acrolein per oral (food and water), respiratory (cigarette smoke, automobile exhaust, and biocide use) and dermal routes, in addition to endogenous generation (metabolism and lipid peroxidation). Acrolein has been suggested to play a role in several disease states including spinal cord injury, multiple sclerosis, Alzheimer's disease, cardiovascular disease, diabetes mellitus, and neuro-, hepato-, and nephro-toxicity. On the cellular level, acrolein exposure has diverse toxic effects, including DNA and protein adduction, oxidative stress, mitochondrial disruption, membrane damage, endoplasmic reticulum stress, and immune dysfunction. This review addresses our current understanding of each pathogenic mechanism of acrolein toxicity, with emphasis on the known and anticipated contribution to clinical disease, and potential therapies.
Keywords: DNA adducts; antioxidants; apoptosis; environmental; exposure; inflammation; oxidative injury.
© The Author 2015. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Society of Toxicology. All rights reserved. For Permissions, please e-mail: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures



References
-
- Abraham K., Andres S., Palavinskas R., Berg K., Appel K. E., Lampen A. (2011). Toxicology and risk assessment of acrolein in food. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 55, 1277–1290. - PubMed
-
- Adams J. D., Jr., Klaidman L. K. (1993). Acrolein-induced oxygen radical formation. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 15, 187–193. - PubMed
-
- Ahmed M. S., Langer H., Abed M., Voelkl J., Lang F. (2013). The uremic toxin acrolein promotes suicidal erythrocyte death. Kidney Blood Press. Res. 37, 158–167. - PubMed
-
- Alarcon R. A. (2012). Anticancer system created by acrolein and hydroxyl radical generated in enzymatic oxidation of spermine and other biochemical reactions. Med. Hypotheses 79, 522–530. - PubMed
-
- Aldini G., Orioli M., Carini M. (2011). Protein modification by acrolein: relevance to pathological conditions and inhibition by aldehyde sequestering agents. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 55, 1301–1319. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

