Astatine-211 conjugated to an anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody eradicates disseminated B-cell lymphoma in a mouse model
- PMID: 25628467
- PMCID: PMC4375108
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2014-11-612770
Astatine-211 conjugated to an anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody eradicates disseminated B-cell lymphoma in a mouse model
Abstract
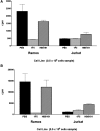
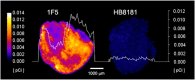
α-Emitting radionuclides deposit a large amount of energy within a few cell diameters and may be particularly effective for radioimmunotherapy targeting minimal residual disease (MRD). To evaluate this hypothesis, (211)At-labeled 1F5 monoclonal antibody (mAb) (anti-CD20) was studied in both bulky lymphoma tumor xenograft and MRD animal models. Superior treatment responses to (211)At-labeled 1F5 mAb were evident in the MRD setting. Lymphoma xenograft tumor-bearing animals treated with doses of up to 48 µCi of (211)At-labeled anti-CD20 mAb ([(211)At]1F5-B10) experienced modest responses (0% cures but two- to threefold prolongation of survival compared with negative controls). In contrast, 70% of animals in the MRD lymphoma model demonstrated complete eradication of disease when treated with (211)At-B10-1F5 at a radiation dose that was less than one-third (15 µCi) of the highest dose given to xenograft animals. Tumor progression among untreated control animals in both models was uniformly lethal. After 130 days, no significant renal or hepatic toxicity was observed in the cured animals receiving 15 µCi of [(211)At]1F5-B10. These findings suggest that α-emitters are highly efficacious in MRD settings, where isolated cells and small tumor clusters prevail.
Figures




References
-
- Fisher RI, Dahlberg S, Nathwani BN, Banks PM, Miller TP, Grogan TM. A clinical analysis of two indolent lymphoma entities: mantle cell lymphoma and marginal zone lymphoma (including the mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue and monocytoid B-cell subcategories): a Southwest Oncology Group study. Blood. 1995;85(4):1075–1082. - PubMed
-
- Dreyling M, Hiddemann W European MCL Network. Current treatment standards and emerging strategies in mantle cell lymphoma. Hematology Am Soc Hematol Educ Program. 2009;2009(1):542–551. - PubMed
-
- Gribben JG, Neuberg D, Freedman AS, et al. Detection by polymerase chain reaction of residual cells with the bcl-2 translocation is associated with increased risk of relapse after autologous bone marrow transplantation for B-cell lymphoma. Blood. 1993;81(12):3449–3457. - PubMed
-
- Gribben JG, Neuberg D, Barber M, et al. Detection of residual lymphoma cells by polymerase chain reaction in peripheral blood is significantly less predictive for relapse than detection in bone marrow. Blood. 1994;83(12):3800–3807. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

