Cisplatin, cetuximab, and radiation in locally advanced head and neck squamous cell cancer: a retrospective review
- PMID: 25628515
- PMCID: PMC4283547
- DOI: 10.4137/CMO.S18682
Cisplatin, cetuximab, and radiation in locally advanced head and neck squamous cell cancer: a retrospective review
Abstract
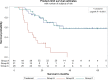
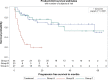
Efficacy of cisplatin versus cetuximab with radiation in locally advanced head and neck cancer (LAHNC) was evaluated. A total of 96 patients with newly diagnosed LAHNC treated at our institution between 2006 and 2011 with concurrent radiation and cisplatin (group A, n = 45), cetuximab (group B, n = 24), or started with cisplatin but switched to cetuximab because of toxicity (group C, n = 27) were reviewed. Chi-square test, analysis of variance, and log-rank test were used for analysis. The three groups had similar baseline characteristics, except for median age, T stage, albumin levels, hemoglobin levels, performance status, and comorbidities. A complete response (CR) was seen in 77%, 17%, and 67% of patients (P < 0.001), respectively. There was no significant difference in median overall survival (OS) between groups A and C. The median OS for groups A and C was not reached (>65 months), even though it was significantly longer than median OS for group B (11.6 months; P ≤ 0.001). The 2-year OS in groups A and C is significantly higher than that in group B (70% for groups A and C, 22% for group B). There is no significant difference in progression-free survival (PFS) between groups A and C. The median PFS for these groups was not reached (>62 months), and is significantly longer than that for group B (4.3 months; P ≤ 0.001). The 2-year PFS of group A (67%) and group C (76%) was significantly longer than that of group B (20%). Cisplatin with radiation appears to be more efficacious even in suboptimal dosing than cetuximab with radiation in LAHNC but the two groups were not well matched.
Keywords: cetuximab; cisplatin; head and neck cancer; overall survival; radiation therapy.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Phase II/III Randomized Controlled Trial of Concomitant Hyperfractionated Radiotherapy plus Cetuximab (Anti-EGFR Antibody) or Chemotherapy in Locally Advanced Head and Neck Cancer.Gulf J Oncolog. 2019 May;1(30):6-12. Gulf J Oncolog. 2019. PMID: 31242976 Clinical Trial.
-
Concurrent cisplatin and radiation versus cetuximab and radiation for locally advanced head-and-neck cancer.Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2011 Nov 15;81(4):915-22. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2010.07.008. Epub 2010 Oct 13. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2011. PMID: 20947269
-
Primary chemoradiation with cisplatin versus cetuximab for locally advanced head and neck cancer: a retrospective cohort study.Exp Hematol Oncol. 2020 Aug 5;9:19. doi: 10.1186/s40164-020-00175-1. eCollection 2020. Exp Hematol Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32775042 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of every 3 week cisplatin or weekly cetuximab with concurrent radiotherapy for locally advanced head and neck cancer.Oral Oncol. 2015 Jul;51(7):704-8. doi: 10.1016/j.oraloncology.2015.04.012. Epub 2015 Apr 30. Oral Oncol. 2015. PMID: 25936651
-
Phase II trial of bevacizumab + cetuximab + cisplatin with concurrent intensity-modulated radiation therapy for patients with stage III/IVB head and neck squamous cell carcinoma.Head Neck. 2016 Apr;38 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):E566-70. doi: 10.1002/hed.24041. Epub 2015 Jul 6. Head Neck. 2016. PMID: 25784616 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
Cited by
-
Cetuximab-Containing Combinations in Locally Advanced and Recurrent or Metastatic Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma.Front Oncol. 2019 May 20;9:383. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2019.00383. eCollection 2019. Front Oncol. 2019. PMID: 31165040 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Survival, recurrence and toxicity of HNSCC in comparison of a radiotherapy combination with cisplatin versus cetuximab: a meta-analysis.BMC Cancer. 2016 Aug 26;16(1):689. doi: 10.1186/s12885-016-2706-2. BMC Cancer. 2016. PMID: 27565887 Free PMC article.
-
Factors that Influence 2-Year Progression-Free Survival Among Head and Neck Cancer Patients.J Epidemiol Glob Health. 2022 Mar;12(1):16-24. doi: 10.1007/s44197-021-00016-2. Epub 2021 Nov 30. J Epidemiol Glob Health. 2022. PMID: 34846716 Free PMC article.
-
[Preclinical models in head and neck tumors : Evaluation of cellular and molecular resistance mechanisms in the tumor microenvironment].HNO. 2016 Dec;64(12):860-869. doi: 10.1007/s00106-016-0276-x. HNO. 2016. PMID: 27837212 Review. German.
-
Retrospective evaluation of concomitant cetuximab and radiotherapy tolerance for locoregional advanced head and neck squamous cell carcinoma treatment in patients unfit for platinum-based chemotherapy.Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2017 Jul;274(7):2883-2889. doi: 10.1007/s00405-017-4550-7. Epub 2017 Apr 5. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2017. PMID: 28382396
References
-
- Ferlay J, Shin HR, Bray F, Forman D, Mathers C, Parkin DM. Estimates of worldwide burden of cancer in 2008: GLOBOCAN 2008. Int J Cancer. 2010;127:2893–917. - PubMed
-
- Monnerat C, Faivre S, Temam S, Bourhis J, Raymond E. End points for new agents in induction chemotherapy for locally advanced head and neck cancers. Ann Oncol. 2002;13:995–1006. - PubMed
-
- Pignon J-P, le Maître A, Maillard E, Bourhis J, MACH-NC Collaborative Group Meta-analysis of chemotherapy in head and neck cancer (MACH-NC): An update on 93 randomised trials and 17,346 patients. Radiother Oncol. 2009;92:4–14. - PubMed
-
- Bonner JA, Harari PM, Giralt J, et al. Radiotherapy plus cetuximab for squamous-cell carcinoma of the head and neck. N Engl J Med. 2006;354(6):567–78. - PubMed
-
- Koutcher L, Sherman E, Fury M, et al. Concurrent cisplatin and radiation versus cetuximab and radiation for locally advanced head and neck cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2011;81(4):915–22. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

