Localization and local translation of Arc/Arg3.1 mRNA at synapses: some observations and paradoxes
- PMID: 25628532
- PMCID: PMC4290588
- DOI: 10.3389/fnmol.2014.00101
Localization and local translation of Arc/Arg3.1 mRNA at synapses: some observations and paradoxes
Abstract
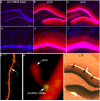
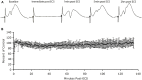
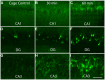
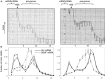
Arc is a unique immediate early gene whose expression is induced as synapses are being modified during learning. The uniqueness comes from the fact that newly synthesized Arc mRNA is rapidly transported throughout dendrites where it localizes near synapses that were recently activated. Here, we summarize aspects of Arc mRNA translation in dendrites in vivo, focusing especially on features of its expression that are paradoxical or that donot fit in with current models of how Arc protein operates. Findings from in vivo studies that donot quite fit include: (1) Following induction of LTP in vivo, Arc mRNA and protein localize near active synapses, but are also distributed throughout dendrites. In contrast, Arc mRNA localizes selectively near active synapses when stimulation is continued as Arc mRNA is transported into dendrites; (2) Strong induction of Arc expression as a result of a seizure does not lead to a rundown of synaptic efficacy in vivo as would be predicted by the hypothesis that high levels of Arc cause glutamate receptor endocytosis and LTD. (3) Arc protein is synthesized in the perinuclear cytoplasm rapidly after transcriptional activation, indicating that at least a pool of Arc mRNA is not translationally repressed to allow for dendritic delivery; (4) Increases in Arc mRNA in dendrites are not paralleled by increases in levels of exon junction complex (EJC) proteins. These results of studies of mRNA trafficking in neurons in vivo provide a new perspective on the possible roles of Arc in activity-dependent synaptic modifications.
Keywords: Arc/Arg3.1; LTP; dendrite; dendritic mRNA; dendritic spines; immediate early genes; protein synthesis; synaptic plasticity.
Figures