Manipulation of the endocytic pathway and phagocyte functions by Mycobacterium tuberculosis lipoarabinomannan
- PMID: 25629008
- PMCID: PMC4290680
- DOI: 10.3389/fcimb.2014.00187
Manipulation of the endocytic pathway and phagocyte functions by Mycobacterium tuberculosis lipoarabinomannan
Abstract
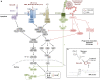
Lipoarabinomannan is a major immunomodulatory lipoglycan found in the cell envelope of Mycobacterium tuberculosis and related human pathogens. It reproduces several salient properties of M. tuberculosis in phagocytic cells, including inhibition of pro-inflammatory cytokine production, inhibition of phagolysosome biogenesis, and inhibition of apoptosis as well as autophagy. In this review, we present our current knowledge on lipoarabinomannan structure and ability to manipulate the endocytic pathway as well as phagocyte functions. A special focus is put on the molecular mechanisms employed and the signaling pathways hijacked. Available information is discussed in the context of M. tuberculosis pathogenesis.
Keywords: Mycobacterium; apoptosis; autophagy; cytokine; lipoarabinomannan; phagosome.
Figures

References
-
- Afonso-Barroso A., Clark S. O., Williams A., Rosa G. T., Nobrega C., Silva-Gomes S., et al. (2012). Lipoarabinomannan mannose caps do not affect mycobacterial virulence or the induction of protective immunity in experimental animal models of infection and have minimal impact on in vitro inflammatory responses. Cell. Microbiol. 15, 660–674. 10.1111/cmi.12065 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

