Gender differences in cerebral regional homogeneity of adult healthy volunteers: a resting-state FMRI study
- PMID: 25629038
- PMCID: PMC4299532
- DOI: 10.1155/2015/183074
Gender differences in cerebral regional homogeneity of adult healthy volunteers: a resting-state FMRI study
Abstract
Objective: We sought to use the regional homogeneity (ReHo) approach as an index in the resting-state functional MRI to investigate the gender differences of spontaneous brain activity within cerebral cortex and resting-state networks (RSNs) in young adult healthy volunteers.
Methods: One hundred and twelve healthy volunteers (56 males, 56 females) participated in the resting-state fMRI scan. The ReHo mappings in the cerebral cortex and twelve RSNs of the male and female groups were compared.
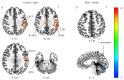
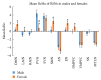
Results: We found statistically significant gender differences in the primary visual network (PVN) (P < 0.004, with Bonferroni correction) and left attention network (LAtN), default mode network (DMN), sensorimotor network (SMN), executive network (EN), and dorsal medial prefrontal network (DMPFC) as well (P < 0.05, uncorrected). The male group showed higher ReHo in the left precuneus, while the female group showed higher ReHo in the right middle cingulate gyrus, fusiform gyrus, left inferior parietal lobule, precentral gyrus, supramarginal gyrus, and postcentral gyrus.
Conclusions: Our results suggested that men and women had regional specific differences during the resting-state. The findings may improve our understanding of the gender differences in behavior and cognition from the perspective of resting-state brain function.
Figures
References
-
- Good C. D., Johnsrude I., Ashburner J., Henson R. N. A., Friston K. J., Frackowiak R. S. J. Cerebral asymmetry and the effects of sex and handedness on brain structure: a voxel-based morphometric analysis of 465 normal adult human brains. NeuroImage. 2001;14(3):685–700. doi: 10.1006/nimg.2001.0857. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Crespo-Facorro B., Roiz-Santiáñez R., Pérez-Iglesias R., et al. Sex-specific variation of MRI-based cortical morphometry in adult healthy volunteers: the effect on cognitive functioning. Progress in Neuro-Psychopharmacology and Biological Psychiatry. 2011;35(2):616–623. doi: 10.1016/j.pnpbp.2011.01.005. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

