TGFβ signaling in myeloid cells regulates mammary carcinoma cell invasion through fibroblast interactions
- PMID: 25629162
- PMCID: PMC4309578
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0117908
TGFβ signaling in myeloid cells regulates mammary carcinoma cell invasion through fibroblast interactions
Abstract
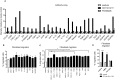
Metastasis is the most devastating aspect of cancer, however we know very little about the mechanisms of local invasion, the earliest step of metastasis. During tumor growth CD11b+ Gr1+ cells, known also as MDSCs, have been shown to promote tumor progression by a wide spectrum of effects that suppress the anti-tumor immune response. In addition to immunosuppression, CD11b+ Gr1+ cells promote metastasis by mechanisms that are currently unknown. CD11b+ Gr1+ cells localize near fibroblasts, which remodel the ECM and leave tracks for collective cell migration of carcinoma cells. In this study we discovered that CD11b+ Gr1+ cells promote invasion of mammary carcinoma cells by increasing fibroblast migration. This effect was directed by secreted factors derived from CD11b+ Gr1+ cells. We have identified several CD11b+ Gr1+ cell secreted proteins that activate fibroblast migration, including CXCL11, CXCL15, FGF2, IGF-I, IL1Ra, Resistin, and Shh. The combination of CXCL11 and FGF2 had the strongest effect on fibroblast migration that is associated with Akt1 and ERK1/2 phosphorylation. Analysis of subsets of CD11b+ Gr1+ cells identified that CD11b+ Ly6Chigh Ly6Glow cells increase fibroblast migration more than other myeloid cell populations. Additionally, tumor-derived CD11b+ Gr1+ cells promote fibroblast migration more than splenic CD11b+ Gr1+ cells of tumor-bearing mice. While TGFβ signaling in fibroblasts does not regulate their migration toward CD11b+ Gr1+ cells, however deletion of TGFβ receptor II on CD11b+ Gr1+ cells downregulates CXCL11, Shh, IGF1 and FGF2 resulting in reduced fibroblast migration. These studies show that TGFβ signaling in CD11b+ Gr1+ cells promotes fibroblast directed carcinoma invasion and suggests that perivascular CD11b+ Ly6Chigh Ly6Glow cells may be the stimulus for localized invasion leading to metastasis.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Richardsen E, Sorbye SW, Crowe JP, Yang JL, Busund LT (2009) Expression of M-CSF and CSF-1R is correlated with histological grade in soft tissue tumors. Anticancer research 29: 3861–3866. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

