Therapeutic efficacy of valproic acid in a combined monocrotaline and chronic hypoxia rat model of severe pulmonary hypertension
- PMID: 25629315
- PMCID: PMC4309681
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0117211
Therapeutic efficacy of valproic acid in a combined monocrotaline and chronic hypoxia rat model of severe pulmonary hypertension
Abstract
Background: Pulmonary hypertension (PH) is a serious disease with poor prognosis. Reports show that cells in remodeled pulmonary arteries of PH patients have similar characteristics to cancer cells, such as exuberant inflammation, increased proliferation, and decreased apoptosis. An ideal strategy for developing PH therapies is to directly target pulmonary vascular remodeling. High levels of histone deacetylase (HDAC) expression and activity are found in certain cancers, and research has shown the potential of HDAC inhibitors in repressing tumor growth via anti-inflammatory and anti-proliferative effects. To date, little is known about the effectiveness of HDAC inhibitors against pulmonary vascular remodeling in severe PH.
Objective: To investigate whether class I HDAC inhibitors suppress or reverse the development of severe PH in rats.
Methods: Male Sprague-Dawley rats were injected with a single, subcutaneous dose of monocrotaline (60 mg/kg), and were exposed to chronic hypoxia to induce severe PH. Valproic acid, a class I HDAC inhibitor, was administered to rats daily via gastric gavage (300 mg/kg) in a PH prevention study (during the first 3 weeks) or a PH reversal study (from 3 to 5 weeks). At the end of experiment, hemodynamic indices were measured, ventricular hypertrophy indices were calculated and vascular remodeling phenotypes were analyzed.
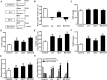
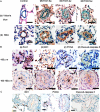
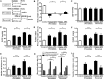
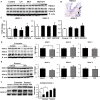
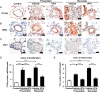
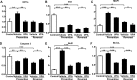
Results: After 3 weeks exposure to a combined stimulation of monocrotaline and chronic hypoxia, rats exhibited a reduced body weight, elevated right ventricular systolic pressure, an increased Fulton index, right ventricle weight ratio, medial wall thickness and muscularized peripheral pulmonary arteries. These parameters for PH evaluation were exacerbated from 3 to 5 weeks. Daily administration of valproic acid therapy prevented and partially reversed the development of severe PH in rats, and decreased inflammation and proliferation in remodeled pulmonary arteries.
Conclusion: These data show that class I HDAC inhibitors may be effective for treating severe PH.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Histone deacetylation inhibition in pulmonary hypertension: therapeutic potential of valproic acid and suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid.Circulation. 2012 Jul 24;126(4):455-67. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.112.103176. Epub 2012 Jun 18. Circulation. 2012. PMID: 22711276 Free PMC article.
-
Lysyl oxidases play a causal role in vascular remodeling in clinical and experimental pulmonary arterial hypertension.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2014 Jul;34(7):1446-58. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.114.303534. Epub 2014 May 15. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2014. PMID: 24833797
-
Evaluation of olmesartan medoxomil in the rat monocrotaline model of pulmonary hypertension.J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2008 Jan;51(1):18-23. doi: 10.1097/FJC.0b013e318159b01c. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2008. PMID: 18209564
-
A review of genetically-driven rodent models of pulmonary hypertension.Vascul Pharmacol. 2022 Jun;144:106970. doi: 10.1016/j.vph.2022.106970. Epub 2022 Feb 10. Vascul Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35150934 Review.
-
Animal models of pulmonary arterial hypertension: the hope for etiological discovery and pharmacological cure.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2009 Dec;297(6):L1013-32. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00217.2009. Epub 2009 Sep 11. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2009. PMID: 19748998 Review.
Cited by
-
Therapeutic Approaches in Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension with Beneficial Effects on Right Ventricular Function-Preclinical Studies.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Oct 24;24(21):15539. doi: 10.3390/ijms242115539. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37958522 Free PMC article. Review.
-
High expression of CXCR4 and stem cell markers in a monocrotaline and chronic hypoxia-induced rat model of pulmonary arterial hypertension.Exp Ther Med. 2018 Jun;15(6):4615-4622. doi: 10.3892/etm.2018.6027. Epub 2018 Apr 3. Exp Ther Med. 2018. PMID: 29805477 Free PMC article.
-
Tsantan Sumtang Alleviates Chronic Hypoxia-Induced Pulmonary Hypertension by Inhibiting Proliferation of Pulmonary Vascular Cells.Biomed Res Int. 2018 Nov 28;2018:9504158. doi: 10.1155/2018/9504158. eCollection 2018. Biomed Res Int. 2018. PMID: 30622966 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of HDAC1 alleviates monocrotaline-induced pulmonary arterial remodeling through up-regulation of miR-34a.Respir Res. 2021 Aug 31;22(1):239. doi: 10.1186/s12931-021-01832-7. Respir Res. 2021. PMID: 34465322 Free PMC article.
-
Perillyle alcohol and Quercetin ameliorate monocrotaline-induced pulmonary artery hypertension in rats through PARP1-mediated miR-204 down-regulation and its downstream pathway.BMC Complement Med Ther. 2020 Jul 13;20(1):218. doi: 10.1186/s12906-020-03015-1. BMC Complement Med Ther. 2020. PMID: 32660602 Free PMC article.
References
-
- McLaughlin VV, Archer SL, Badesch DB, Barst RJ, Farber HW, et al. (2009) ACCF/AHA 2009 expert consensus document on pulmonary hypertension: a report of the American College of Cardiology Foundation Task Force on Expert Consensus Documents and the American Heart Association developed in collaboration with the American College of Chest Physicians; American Thoracic Society, Inc; and the Pulmonary Hypertension Association. J Am Coll Cardiol 53:1573–1619. 10.1016/j.jacc.2009.01.004 - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

