Sulphated polysaccharides from Ulva clathrata and Cladosiphon okamuranus seaweeds both inhibit viral attachment/entry and cell-cell fusion, in NDV infection
- PMID: 25629385
- PMCID: PMC4344596
- DOI: 10.3390/md13020697
Sulphated polysaccharides from Ulva clathrata and Cladosiphon okamuranus seaweeds both inhibit viral attachment/entry and cell-cell fusion, in NDV infection
Abstract
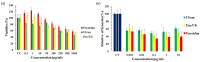
Sulphated polysaccharides (SP) extracted from seaweeds have antiviral properties and are much less cytotoxic than conventional drugs, but little is known about their mode of action. Combination antiviral chemotherapy may offer advantages over single agent therapy, increasing efficiency, potency and delaying the emergence of resistant virus. The paramyxoviridae family includes pathogens causing morbidity and mortality worldwide in humans and animals, such as the Newcastle Disease Virus (NDV) in poultry. This study aims at determining the antiviral activity and mechanism of action in vitro of an ulvan (SP from the green seaweed Ulva clathrata), and of its mixture with a fucoidan (SP from Cladosiphon okamuranus), against La Sota NDV strain. The ulvan antiviral activity was tested using syncytia formation, exhibiting an IC50 of 0.1 μg/mL; ulvan had a better anti cell-cell spread effect than that previously shown for fucoidan, and inhibited cell-cell fusion via a direct effect on the F0 protein, but did not show any virucidal effect. The mixture of ulvan and fucoidan showed a greater anti-spread effect than SPs alone, but ulvan antagonizes the effect of fucoidan on the viral attachment/entry. Both SPs may be promising antivirals against paramyxovirus infection but their mixture has no clear synergistic advantage.
Figures



References
-
- Elizondo-Gonzalez R., Cruz-Suarez L.E., Ricque-Marie D., Mendoza-Gamboa E., Rodriguez-padilla C., Trejo-Avila L.M. In vitro characterization of the antiviral activity of fucoidan from Cladosiphon okamuranus against Newcastle Disease Virus. Virol. J. 2012;9:307. doi: 10.1186/1743-422X-9-307. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Trejo-Avila L.M., Morales-Martínez M.L., Ricque-Marie D., Cruz-Suarez L.E., Zapata-Benavides P., Morán-Santibañez K., Rodríguez-Padilla C. In vitro anti-canine distemper virus activity of fucoidan extracted from the brown alga Cladosiphon okamuranus. Virus Dis. 2014;25:474–480. doi: 10.1007/s13337-014-0228-6. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Patarra R.F., Paiva L., Neto A.I., Lima E., Baptista J. Nutritional value of selected macroalgae. J. Appl. Phycol. 2011;23:205–208. doi: 10.1007/s10811-010-9556-0. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

