Discovery of antibiotic (E)-3-(3-carboxyphenyl)-2-(4-cyanostyryl)quinazolin-4(3H)-one
- PMID: 25629446
- PMCID: PMC4607046
- DOI: 10.1021/jacs.5b00056
Discovery of antibiotic (E)-3-(3-carboxyphenyl)-2-(4-cyanostyryl)quinazolin-4(3H)-one
Abstract
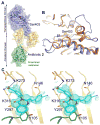
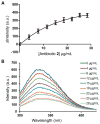
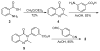
In the face of the clinical challenge posed by resistant bacteria, the present needs for novel classes of antibiotics are genuine. In silico docking and screening, followed by chemical synthesis of a library of quinazolinones, led to the discovery of (E)-3-(3-carboxyphenyl)-2-(4-cyanostyryl)quinazolin-4(3H)-one (compound 2) as an antibiotic effective in vivo against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA). This antibiotic impairs cell-wall biosynthesis as documented by functional assays, showing binding of 2 to penicillin-binding protein (PBP) 2a. We document that the antibiotic also inhibits PBP1 of S. aureus, indicating a broad targeting of structurally similar PBPs by this antibiotic. This class of antibiotics holds promise in fighting MRSA infections.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures
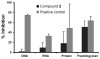

References
-
- Boucher HW, Talbot GH, Bradley JS, Edwards JE, Jr, Gilbert D, Rice LB, Scheld M, Spellburg B, Bartlett J. Clin Infect Dis. 2009;48:1. - PubMed
-
- Pendleton JN, Gorman SP, Gilmore BF. Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther. 2013;11:297. - PubMed
-
- Lim D, Strynadka NCJ. Nat Struct Biol. 2002;9:870. - PubMed
-
- Glide. Schrödinger, LLC; New York, NY: 2009.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

