Convergent evolution of AUA decoding in bacteria and archaea
- PMID: 25629511
- PMCID: PMC4615378
- DOI: 10.4161/15476286.2014.992281
Convergent evolution of AUA decoding in bacteria and archaea
Abstract
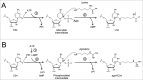
Deciphering AUA codons is a difficult task for organisms, because AUA and AUG specify isoleucine (Ile) and methionine (Met), separately. Each of the other purine-ending sense co-don sets (NNR) specifies a single amino acid in the universal genetic code. In bacteria and archaea, the cytidine derivatives, 2-lysylcytidine (L or lysidine) and 2-agmatinylcytidine (agm(2)C or agmatidine), respectively, are found at the first letter of the anticodon of tRNA(Ile) responsible for AUA codons. These modifications prevent base pairing with G of the third letter of AUG codon, and enable tRNA(Ile) to decipher AUA codon specifically. In addition, these modifications confer a charging ability of tRNA(Ile) with Ile. Despite their similar chemical structures, L and agm(2)C are synthesized by distinctive mechanisms and catalyzed by different classes of enzymes, implying that the analogous decoding systems for AUA codons were established by convergent evolution after the phylogenic split between bacteria and archaea-eukaryotes lineages following divergence from the last universal common ancestor (LUCA).
Figures





References
-
- Ogle JM, Murphy FV, Tarry MJ, Ramakrishnan V. Selection of tRNA by the ribosome requires a transition from an open to a closed form. Cell 2002; 111:721-32; PMID:12464183; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1016/S0092-8674(02)01086-3 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ogle JM, Brodersen DE, Clemons WM, Jr, Tarry MJ, Carter AP, Ramakrishnan V. Recognition of cognate transfer RNA by the 30S ribosomal subunit. Science 2001; 292:897-902; PMID:11340196; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1126/science.1060612 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Schmeing TM, Voorhees RM, Kelley AC, Gao YG, Murphy FV, 4th, Weir JR, Ramakrishnan V. The crystal structure of the ribosome bound to EF-Tu and aminoacyl-tRNA. Science 2009; 326:688-94; PMID:19833920; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1126/science.1179700 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Voorhees RM, Schmeing TM, Kelley AC, Ramakrishnan V. The mechanism for activation of GTP hydrolysis on the ribosome. Science 2010; 330:835-8; PMID:21051640; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1126/science.1194460 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Crick FH. Codon–anticodon pairing: the wobble hypothesis. J Mol Biol 1966; 19:548-55; PMID:5969078; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1016/S0022-2836(66)80022-0 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
