Dendritic cells and innate immunity in kidney transplantation
- PMID: 25629552
- PMCID: PMC4382394
- DOI: 10.1038/ki.2014.430
Dendritic cells and innate immunity in kidney transplantation
Abstract
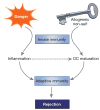
This review summarizes emerging concepts related to the roles of dendritic cells (DCs) and innate immunity in organ transplant rejection. First, it highlights the primary role that recipient, rather than donor, DCs have in rejection and reviews their origin and function in the transplanted kidney. Second, it introduces the novel concept that recognition of allogeneic non-self by host monocytes (referred to here as innate allorecognition) is necessary for initiating rejection by inducing monocyte differentiation into mature, antigen-presenting DCs. Both concepts provide opportunities for preventing rejection by targeting monocytes or DCs.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no interests to disclose.
Figures
References
-
- USRDS. Atlas of ESRD. 2013 http://www.usrds.org/2013/view/Default.aspx.
-
- Abbas AK, Janeway CA., Jr Immunology: improving on nature in the twenty-first century. Cell. 2000;100:129–38. - PubMed
-
- Janeway CA., Jr Approaching the asymptote? Evolution and revolution in immunology. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1989;54(Pt 1):1–13. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

