Ruxolitinib versus standard therapy for the treatment of polycythemia vera
- PMID: 25629741
- PMCID: PMC4358820
- DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa1409002
Ruxolitinib versus standard therapy for the treatment of polycythemia vera
Abstract
Background: Ruxolitinib, a Janus kinase (JAK) 1 and 2 inhibitor, was shown to have a clinical benefit in patients with polycythemia vera in a phase 2 study. We conducted a phase 3 open-label study to evaluate the efficacy and safety of ruxolitinib versus standard therapy in patients with polycythemia vera who had an inadequate response to or had unacceptable side effects from hydroxyurea.
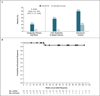
Methods: We randomly assigned phlebotomy-dependent patients with splenomegaly, in a 1:1 ratio, to receive ruxolitinib (110 patients) or standard therapy (112 patients). The primary end point was both hematocrit control through week 32 and at least a 35% reduction in spleen volume at week 32, as assessed by means of imaging.
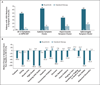
Results: The primary end point was achieved in 21% of the patients in the ruxolitinib group versus 1% of those in the standard-therapy group (P<0.001). Hematocrit control was achieved in 60% of patients receiving ruxolitinib and 20% of those receiving standard therapy; 38% and 1% of patients in the two groups, respectively, had at least a 35% reduction in spleen volume. A complete hematologic remission was achieved in 24% of patients in the ruxolitinib group and 9% of those in the standard-therapy group (P=0.003); 49% versus 5% had at least a 50% reduction in the total symptom score at week 32. In the ruxolitinib group, grade 3 or 4 anemia occurred in 2% of patients, and grade 3 or 4 thrombocytopenia occurred in 5%; the corresponding percentages in the standard-therapy group were 0% and 4%. Herpes zoster infection was reported in 6% of patients in the ruxolitinib group and 0% of those in the standard-therapy group (grade 1 or 2 in all cases). Thromboembolic events occurred in one patient receiving ruxolitinib and in six patients receiving standard therapy.
Conclusions: In patients who had an inadequate response to or had unacceptable side effects from hydroxyurea, ruxolitinib was superior to standard therapy in controlling the hematocrit, reducing the spleen volume, and improving symptoms associated with polycythemia vera. (Funded by Incyte and others; RESPONSE ClinicalTrials.gov number, NCT01243944.).
Figures

Comment in
-
Ruxolitinib versus standard therapy for the treatment of polycythemia vera.N Engl J Med. 2015 Apr 23;372(17):1670-1. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc1502524. N Engl J Med. 2015. PMID: 25901432 No abstract available.
-
Ruxolitinib versus standard therapy for the treatment of polycythemia vera.N Engl J Med. 2015 Apr 23;372(17):1670. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc1502524. N Engl J Med. 2015. PMID: 25901433 No abstract available.
References
-
- Spivak JL. Polycythemia vera: myths, mechanisms, and management. Blood. 2002;100:4272–4290. - PubMed
-
- Tefferi A. Polycythemia vera and essential thrombocythemia: 2013 update on diagnosis, risk-stratification, and management. Am J Hematol. 2013;88:507–516. - PubMed
-
- Stuart BJ, Viera AJ. Polycythemia vera. Am Fam Physician. 2004;69:2139–2144. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
