The effect of HAART-induced HIV suppression on circulating markers of inflammation and immune activation
- PMID: 25630041
- PMCID: PMC4311407
- DOI: 10.1097/QAD.0000000000000545
The effect of HAART-induced HIV suppression on circulating markers of inflammation and immune activation
Abstract
Objectives: To investigate the impact of HAART-induced HIV suppression on levels of 24 serological biomarkers of inflammation and immune activation.
Design: A prospective cohort study.
Methods: Biomarkers were measured with multiplex assays in centralized laboratories using stored serum samples contributed by 1697 men during 8903 person-visits in the Multicenter AIDS Cohort Study (MACS) from 1984 to 2009. Using generalized gamma models, we compared biomarker values across three groups, adjusting for possible confounders: HIV-uninfected (NEG); HIV-positive, HAART-naive (NAI); and HAART-exposed with HIV RNA suppressed to less than 50 copies/ml plasma (SUP). We also estimated changes in biomarker levels associated with duration of HIV suppression, using splined generalized gamma regression with a knot at 1 year.
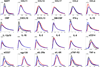
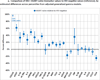
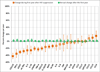
Results: Most biomarkers were relatively normalized in the SUP group relative to the NAI group; however, 12 biomarkers in the SUP group were distinct (P < 0.002) from NEG values: CXCL10, C-reactive protein (CRP), sCD14, sTNFR2, tumour necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α), sCD27, sGP130, interleukin (IL)-8, CCL13, BAFF, GM-CSF and IL-12p70. Thirteen biomarkers exhibited significant changes in the first year after viral suppression, but none changed significantly after that time.
Conclusion: Biomarkers of inflammation and immune activation moved towards HIV-negative levels within the first year after HAART-induced HIV suppression. Although several markers of T-cell activation returned to levels present in HIV-negative men, residual immune activation, particularly monocyte/macrophage activation, was present. This residual immune activation may represent a therapeutic target to improve the prognosis of HIV-infected individuals receiving HAART.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Detels R, Muñoz A, McFarlane G, Kingsley LA, Margolick JB, Giorgi J, et al. Effectiveness of potent antiretroviral therapy on time to AIDS and death in men with known HIV infection duration. Multicenter AIDS Cohort Study Investigators. JAMA. 1998;280:1497–1503. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- U01 AI035042/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR025005/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001079/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UO1-AI-35042/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UO1-AI-35040/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UO1-AI-35041/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI035041/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1-AI-35043/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI035043/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG028748/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- UL1-RR025005/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- 5P30 AG028748/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- UO1-AI-35039/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI068613/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI035040/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI035039/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

