The 5' and 3' ends of alphavirus RNAs--Non-coding is not non-functional
- PMID: 25630058
- PMCID: PMC4654126
- DOI: 10.1016/j.virusres.2015.01.016
The 5' and 3' ends of alphavirus RNAs--Non-coding is not non-functional
Abstract
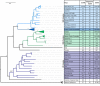
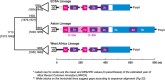
The non-coding regions found at the 5' and 3' ends of alphavirus genomes regulate viral gene expression, replication, translation and virus-host interactions, which have significant implications for viral evolution, host range, and pathogenesis. The functions of these non-coding regions are mediated by a combination of linear sequence and structural elements. The capped 5' untranslated region (UTR) contains promoter elements, translational regulatory sequences that modulate dependence on cellular translation factors, and structures that help to avoid innate immune defenses. The polyadenylated 3' UTR contains highly conserved sequence elements for viral replication, binding sites for cellular miRNAs that determine cell tropism, host range, and pathogenesis, and conserved binding regions for a cellular protein that influences viral RNA stability. Nonetheless, there are additional conserved elements in non-coding regions of the virus (e.g., the repeated sequence elements in the 3' UTR) whose function remains obscure. Thus, key questions remain as to the function of these short yet influential untranslated segments of alphavirus RNAs.
Keywords: Polyadenylation; Protein–RNA interactions; Translation regulation; Viral pathogenesis; mRNA capping; miRNAs.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Berben-Bloemheuvel G., Kasperaitis M.A., van Heugten H., Thomas A.A., van Steeg H., Voorma H.O. Interaction of initiation factors with the cap structure of chimaeric mRNA containing the 5′-untranslated regions of Semliki Forest virus RNA is related to translational efficiency. Eur. J. Biochem./FEBS. 1992;208:581–587. - PubMed
-
- Bogerd H.P., Skalsky R.L., Kennedy E.M., Furuse Y., Whisnant A.W., Flores O., Schultz K.L., Putnam N., Barrows N.J., Sherry B., Scholle F., Garcia-Blanco M.A., Griffin D.E., Cullen B.R. Replication of many human viruses is refractory to inhibition by endogenous cellular microRNAs. J. Virol. 2014;88:8065–8076. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

