Ageing and neurotrophic signalling effects on diaphragm neuromuscular function
- PMID: 25630263
- PMCID: PMC4303387
- DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2014.282244
Ageing and neurotrophic signalling effects on diaphragm neuromuscular function
Abstract
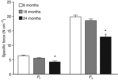
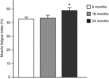
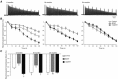
The age-related mechanisms underlying sarcopenia are largely unknown. We hypothesize that age-related neuromuscular changes depend on brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) acting through the tropomyosin-related kinase receptor B (TrkB). Maximal specific force and neuromuscular transmission failure were assessed at 6, 18 and 24 months following control, BDNF or phosphoprotein phosphatase 1 derivative (1NMPP1) treatment in male TrkB(F616A) mice. Phosphoprotein phosphatase-1 derivatives such as 1NMPP1 inhibit TrkB kinase activity as a result of this single amino acid mutation in the ATP binding domain. Maximal twitch and isometric tetanic force were reduced at 24 months compared to 6 and 18 months (P < 0.001). Neuromuscular transmission failure significantly increased at 18 and 24 months compared to 6 months (age × treatment interaction: P < 0.001). Neuromuscular transmission was improved following BDNF at 6 and 18 months and was impaired only at 6 months following 1NMPP1 treatment. Age and inhibition of TrkB kinase activity had similar effects on neuromuscular transmission failure, supporting a critical role for BDNF/TrkB signalling on neuromuscular changes in ageing. These results suggest that an age-related loss of endogenous BDNF precedes reductions in TrkB kinase activity in the diaphragm muscle.
© 2014 The Authors. The Journal of Physiology © 2014 The Physiological Society.
Figures
References
-
- Ameredes BT, Zhan W-Z, Vanderboom R, Prakash YS. Sieck GC. Power fatigue of the rat diaphragm muscle. J Appl Physiol. 2000;89:2215–2219. - PubMed
-
- Calabrese F, Guidotti G, Racagni G. Riva MA. Reduced neuroplasticity in aged rats: a role for the neurotrophin brain-derived neurotrophic factor. Neurobiol Aging. 2013;34:2768–2776. - PubMed
-
- Chen X, Ye H, Kuruvilla R, Ramanan N, Scangos KW, Zhang C, Johnson NM, England PM, Shokat KM. Ginty DD. A chemical–genetic approach to studying neurotrophin signaling. Neuron. 2005;46:13–21. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

