Deterministic identification of specific individuals from GWAS results
- PMID: 25630377
- PMCID: PMC4443672
- DOI: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btv018
Deterministic identification of specific individuals from GWAS results
Abstract
Motivation: Genome-wide association studies (GWASs) are commonly applied on human genomic data to understand the causal gene combinations statistically connected to certain diseases. Patients involved in these GWASs could be re-identified when the studies release statistical information on a large number of single-nucleotide polymorphisms. Subsequent work, however, found that such privacy attacks are theoretically possible but unsuccessful and unconvincing in real settings.
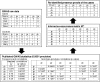
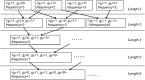
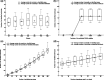
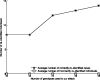
Results: We derive the first practical privacy attack that can successfully identify specific individuals from limited published associations from the Wellcome Trust Case Control Consortium (WTCCC) dataset. For GWAS results computed over 25 randomly selected loci, our algorithm always pinpoints at least one patient from the WTCCC dataset. Moreover, the number of re-identified patients grows rapidly with the number of published genotypes. Finally, we discuss prevention methods to disable the attack, thus providing a solution for enhancing patient privacy.
Availability and implementation: Proofs of the theorems and additional experimental results are available in the support online documents. The attack algorithm codes are publicly available at https://sites.google.com/site/zhangzhenjie/GWAS_attack.zip. The genomic dataset used in the experiments is available at http://www.wtccc.org.uk/ on request.
© The Author 2015. Published by Oxford University Press. All rights reserved. For Permissions, please e-mail: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures
References
-
- Agrawal R., et al. (1994) Fast algorithms for mining association rules. In: Bocca,J.B. et al. (eds) Proceedings of the 20th International Conference of Very Large Data Bases, VLDB , Springer, New York, NY, USA; Vol. 1215, pp. 487–499.
-
- Fraser J.A., et al. . (2005) Same-sex mating and the origin of the Vancouver Island Cryptococcus gattii outbreak. Nature , 437, 1360–1364. - PubMed
-
- Haines J.L., Pericak-Vance M.A. (2006) Genetic Analysis of Complex Disease . Hoboken, New Jersey, USA, John Wiley & Sons.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

