Psychological distress following marital separation interacts with a polymorphism in the serotonin transporter gene to predict cardiac vagal control in the laboratory
- PMID: 25630596
- PMCID: PMC4437920
- DOI: 10.1111/psyp.12409
Psychological distress following marital separation interacts with a polymorphism in the serotonin transporter gene to predict cardiac vagal control in the laboratory
Abstract
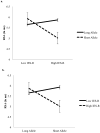
Marital separation is linked to negative mental and physical health; however, the strength of this link may vary across people. This study examined changes in respiratory sinus arrhythmia (RSA), used to assess cardiac vagal control, in recently separated adults (N = 79; M time since separation = 3.5 months). When reflecting on the separation, self-reported psychological distress following the separation interacted with a polymorphism in the serotonin transporter gene (5-HTTLPR) and a relevant single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP), rs25531, to predict RSA. Among people reporting emotional difficulties after the separation, those who were homozygous for the short allele had lower RSA levels while reflecting on their relationship than other genotypes. The findings, although limited by the relatively small sample size, are discussed in terms of how higher-sensitivity genotypes may interact with psychological responses to stress to alter physiology.
Keywords: Divorce; Heart rate variability; Marital separation; Respiratory sinus arrhythmia; Serotonin transporter gene (5-HTTLPR); Single nucleotide polymorphism.
© 2015 Society for Psychophysiological Research.
Figures
References
-
- Anchodoquy C, McGeary C, Liu L, Krauter KS. Genotyping of three candidate genes after whole-genome preamplification of DNA collected from buccal cells. Behavior Genetics. 2003;33:73–77. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

