An ATRActive future for differentiation therapy in AML
- PMID: 25631637
- PMCID: PMC4494875
- DOI: 10.1016/j.blre.2015.01.002
An ATRActive future for differentiation therapy in AML
Abstract
The success of all-trans retinoic acid (ATRA) therapy in acute promeylocytic leukemia (APL) has spawned numerous attempts to translate the paradigm of differentiation therapy to non-APL acute myelocytic leukemia (AML). However, the results of clinical trials have been overall disappointing. In this review we discuss the mechanism of retinoic acid signaling and the results of major clinical trials that have attempted to incorporate ATRA into AML regimens. We discuss recent evidence that indicate that the retinoic acid signaling pathway may be dysfunctional in AML. Preliminary studies suggest that targeting the pathways that modify retinoic acid receptor activity may reactivate the dormant retinoic acid-signaling pathway. Such strategies may revive the ability of ATRA to induce myeloid differentiation and apoptosis in non-APL AML.
Keywords: AML; ATRA; differentiation therapy.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
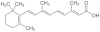



References
-
- Melnick A, Licht JD. Deconstructing a disease: RARalpha, its fusion partners, and their roles in the pathogenesis of acute promyelocytic leukemia. Blood. 1999;93:3167–215. - PubMed
-
- de The H, Lavau C, Marchio A, Chomienne C, Degos L, Dejean A. The PML-RAR alpha fusion mRNA generated by the t(15;17) translocation in acute promyelocytic leukemia encodes a functionally altered RAR. Cell. 1991;66:675–84. - PubMed
-
- Kakizuka A, Miller WH, Jr., Umesono K, Warrell RP, Jr., Frankel SR, Murty VV, et al. Chromosomal translocation t(15;17) in human acute promyelocytic leukemia fuses RAR alpha with a novel putative transcription factor, PML. Cell. 1991;66:663–74. - PubMed
-
- Nasr R, Guillemin MC, Ferhi O, Soilihi H, Peres L, Berthier C, et al. Eradication of acute promyelocytic leukemia-initiating cells through PML-RARA degradation. Nat Med. 2008;14:1333–42. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

