Tracking donor-reactive T cells: Evidence for clonal deletion in tolerant kidney transplant patients
- PMID: 25632034
- PMCID: PMC4360892
- DOI: 10.1126/scitranslmed.3010760
Tracking donor-reactive T cells: Evidence for clonal deletion in tolerant kidney transplant patients
Abstract
T cell responses to allogeneic major histocompatibility complex antigens present a formidable barrier to organ transplantation, necessitating long-term immunosuppression to minimize rejection. Chronic rejection and drug-induced morbidities are major limitations that could be overcome by allograft tolerance induction. Tolerance was first intentionally induced in humans via combined kidney and bone marrow transplantation (CKBMT), but the mechanisms of tolerance in these patients are incompletely understood. We now establish an assay to identify donor-reactive T cells and test the role of deletion in tolerance after CKBMT. Using high-throughput sequencing of the T cell receptor B chain CDR3 region, we define a fingerprint of the donor-reactive T cell repertoire before transplantation and track those clones after transplant. We observed posttransplant reductions in donor-reactive T cell clones in three tolerant CKBMT patients; such reductions were not observed in a fourth, nontolerant, CKBMT patient or in two conventional kidney transplant recipients on standard immunosuppressive regimens. T cell repertoire turnover due to lymphocyte-depleting conditioning only partially accounted for the observed reductions in tolerant patients; in fact, conventional transplant recipients showed expansion of circulating donor-reactive clones, despite extensive repertoire turnover. Moreover, loss of donor-reactive T cell clones more closely associated with tolerance induction than in vitro functional assays. Our analysis supports clonal deletion as a mechanism of allograft tolerance in CKBMT patients. The results validate the contribution of donor-reactive T cell clones identified before transplant by our method, supporting further exploration as a potential biomarker of transplant outcomes.
Copyright © 2015, American Association for the Advancement of Science.
Figures
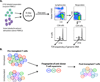

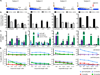


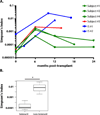
Comment in
-
I spy alloreactive T cells.Sci Transl Med. 2015 Jan 28;7(272):272fs3. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.aaa5083. Sci Transl Med. 2015. PMID: 25632032
-
Immunology: Clonal deletion contributes to allograft tolerance.Nat Rev Nephrol. 2015 Apr;11(4):196. doi: 10.1038/nrneph.2015.16. Epub 2015 Feb 17. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2015. PMID: 25686571 No abstract available.
-
Comment on "Tracking donor-reactive T cells: Evidence for clonal deletion in tolerant kidney transplant patients".Sci Transl Med. 2015 Jul 22;7(297):297le1. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.aab1994. Sci Transl Med. 2015. PMID: 26203079 No abstract available.
-
Author response to comment on "Tracking donor-reactive T cells: Evidence for clonal deletion in tolerant kidney transplant patients".Sci Transl Med. 2015 Jul 22;7(297):297lr1. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.aac9461. Sci Transl Med. 2015. PMID: 26203080 No abstract available.
References
-
- Fehr T, Sykes M. Tolerance induction in clinical transplantation. Transplant immunology. 2004;13:117–130. - PubMed
-
- Lamb KE, Lodhi S, Meier-Kriesche HU. Long-term renal allograft survival in the United States: a critical reappraisal. American journal of transplantation. 2011;11:450–462. - PubMed
-
- Brouard S, Le Bars A, Dufay A, Gosselin M, Foucher Y, Guillet M, Cesbron-Gautier A, Thervet E, Legendre C, Dugast E, Pallier A, Guillot-Gueguen C, Lagoutte L, Evanno G, Giral M, Soulillou JP. Identification of a gene expression profile associated with operational tolerance among a selected group of stable kidney transplant patients. Transpl Int. 2011;24:536–547. - PubMed
-
- Cippa PE, Fehr T. Spontaneous tolerance in kidney transplantation--an instructive, but very rare paradigm. Transpl Int. 2011;24:534–535. - PubMed
-
- Fudaba Y, Spitzer TR, Shaffer J, Kawai T, Fehr T, Delmonico F, Preffer F, Tolkoff-Rubin N, Dey BR, Saidman SL, Kraus A, Bonnefoix T, McAfee S, Power K, Kattleman K, Colvin RB, Sachs DH, Cosimi AB, Sykes M. Myeloma responses and tolerance following combined kidney and nonmyeloablative marrow transplantation: in vivo and in vitro analyses. American journal of transplantation. 2006;6:2121–2133. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

