Exosomes in mesenchymal stem cells, a new therapeutic strategy for cardiovascular diseases?
- PMID: 25632267
- PMCID: PMC4308409
- DOI: 10.7150/ijbs.10725
Exosomes in mesenchymal stem cells, a new therapeutic strategy for cardiovascular diseases?
Abstract
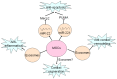
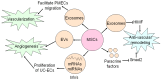
Cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) are still a major cause of people deaths worldwide, and mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) transplantation holds great promise due to its capacity to differentiate into cardiovascular cells and secrete protective cytokines, which presents an important mechanism of MSCs therapy for CVDs. Although the capability of MSCs to differentiate into cardiomyocytes (CMCs), endothelial cells (ECs) and vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs) has been well recognized in massive previous experiments both in vitro and in vivo, low survival rate of transplanted MSCs in recipient hearts suggests that therapeutic effects of MSCs transplantation might be also correlated with other underlying mechanisms. Notably, recent studies uncovered that MSCs were able to secret cholesterol-rich, phospholipid exosomes which were enriched with microRNAs (miRNAs). The released exosomes from MSCs acted on hearts and vessels, and then exerted anti-apoptosis, cardiac regeneration, anti-cardiac remodeling, anti-inflammatory effects, neovascularization and anti-vascular remodeling, which are considered as novel molecular mechanisms of therapeutic potential of MSCs transplantation. Here we summarized recent advances about the role of exosomes in MSCs therapy for CVDs, and discussed exosomes as a novel approach in the treatment of CVDs in the future.
Keywords: exosomes; mesenchymal stem cell; microRNA; myocardial infarction; pulmonary hypertension; reperfusion injury.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures
References
-
- Christoforou N, Gearhart JD. Stem cells and their potential in cell-based cardiac therapies. Prog Cardiovasc Dis. 2007;49:396–413. doi: 10.1016/j.pcad.2007.02.006. - PubMed
-
- Wu JY, Liao C, Xu ZP, Chen JS, Gu SL. [A modified method to isolate and identify the adult mesenchymal stem cells from human bone marrow] Zhongguo Shi Yan Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 2006;14:557–60. - PubMed
-
- Mazzetti MP, Oliveira IS, Miranda-Ferreira R, Fauaz G, Ribeiro CN, Gomes PO. et al. Qualitative and quantitative analysis of rabbit's fat mesenchymal stem cells. Acta Cir Bras. 2010;25:24–7. - PubMed
-
- Zhang MW, Guo ZK, Liu XD, Wu Y, Hou CM, Mao N. [Development of methodology for isolation and culture of mesenchymal stem cells derived from mouse skeletal muscle] Zhongguo Shi Yan Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 2003;11:538–41. doi:1009-2137(2003)05-0538-04. - PubMed
-
- Ling L, Ni Y, Wang Q, Wang H, Hao S, Hu Y. et al. Transdifferentiation of mesenchymal stem cells derived from human fetal lung to hepatocyte-like cells. Cell Biol Int. 2008;32:1091–8. doi:10.1016/j.cellbi.2008.04.020. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

