End-organ protection in hypertension by the novel and selective Rho-kinase inhibitor, SAR407899
- PMID: 25632317
- PMCID: PMC4306204
- DOI: 10.4330/wjc.v7.i1.31
End-organ protection in hypertension by the novel and selective Rho-kinase inhibitor, SAR407899
Abstract
Aim: To compare the therapeutic efficacy of SAR407899 with the current standard treatment for hypertension [an angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE)-inhibitor and a calcium channel blocker] and compare the frequency and severity of the hypertension-related end-organ damage.
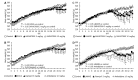
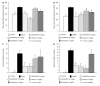
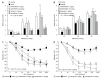
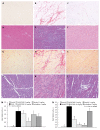
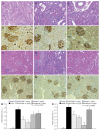
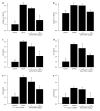
Methods: Long-term pharmacological characte-rization of SAR407899 has been performed in two animal models of hypertension, of which one is sensitive to ACE-inhibition (LNAME) and the other is insensitive [deoxycorticosterone acetate (DOCA)]. SAR407899 efficiently lowered high blood pressure and significantly reduced late-stage end organ damage as indicated by improved heart, kidney and endothelial function and reduced heart and kidney fibrosis in both models of chronic hypertension.
Results: Long term treatment with SAR407899 has been well tolerated and dose-dependently reduced elevated blood pressure in both models with no signs of tachyphylaxia. Blood pressure lowering effects and protective effects on hypertension related end organ damage of SAR407899 were superior to ramipril and amlodipine in the DOCA rat. Typical end-organ damage was significantly reduced in the SAR407899-treated animals. Chronic administration of SAR407899 significantly reduced albuminuria in both models. The beneficial effect of SAR407899 was associated with a reduction in leukocyte/macrophage tissue infiltration. The overall protective effect of SAR407899 was superior or comparable to that of ACE-inhibition or calcium channel blockade. Chronic application of SAR407899 protects against hypertension and hypertension-induced end organ damage, regardless of the pathophysiological mechanism of hypertension.
Conclusion: Rho-kinases-inhibition by the SAR407899 represents a new therapeutic option for the treatment of hypertension and its complications.
Keywords: Angiotensin converting enzyme-inhibition; End organ damage; Hypertension; Rho-kinase.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Pharmacological characterization of SAR407899, a novel rho-kinase inhibitor.Hypertension. 2009 Sep;54(3):676-83. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.109.134353. Epub 2009 Jul 13. Hypertension. 2009. PMID: 19597037
-
The Rho kinase inhibitor SAR407899 potently inhibits endothelin-1-induced constriction of renal resistance arteries.J Hypertens. 2012 May;30(5):980-9. doi: 10.1097/HJH.0b013e328351d459. J Hypertens. 2012. PMID: 22388233
-
Effects of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor and angiotensin type 1 receptor antagonist in deoxycorticosterone acetate-salt hypertensive mice lacking Ren-2 gene.Hypertension. 2001 Mar;37(3):974-80. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.37.3.974. Hypertension. 2001. PMID: 11244026
-
Effects of renin-angiotensin system inhibition on end-organ protection: can we do better?Clin Ther. 2007 Sep;29(9):1803-24. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2007.09.019. Clin Ther. 2007. PMID: 18035185 Review.
-
Angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors, calcium channel blockers, and their combination in the treatment of glomerular disease.J Hypertens Suppl. 1997 Mar;15(2):S21-6. J Hypertens Suppl. 1997. PMID: 9218194 Review.
Cited by
-
Investigational Rho Kinase Inhibitors for the Treatment of Glaucoma.J Exp Pharmacol. 2021 Feb 25;13:197-212. doi: 10.2147/JEP.S259297. eCollection 2021. J Exp Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33664600 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Effects of ROCK Inhibitor on Prevention of Dexamethasone-Induced Glaucoma Phenotype in Human Trabecular Meshwork Cells.Transl Vis Sci Technol. 2023 Dec 1;12(12):4. doi: 10.1167/tvst.12.12.4. Transl Vis Sci Technol. 2023. PMID: 38051267 Free PMC article.
-
Matrix Metalloproteinase 1 Causes Vasoconstriction and Enhances Vessel Reactivity to Angiotensin II via Protease-Activated Receptor 1.Reprod Sci. 2016 Apr;23(4):542-8. doi: 10.1177/1933719115607998. Epub 2015 Oct 4. Reprod Sci. 2016. PMID: 26438597 Free PMC article.
-
Rho-Kinase Inhibition of Active Force and Passive Tension in Airway Smooth Muscle: A Strategy for Treating Airway Hyperresponsiveness in Asthma.Biology (Basel). 2024 Feb 11;13(2):115. doi: 10.3390/biology13020115. Biology (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38392332 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bidani AK, Griffin KA. Long-term renal consequences of hypertension for normal and diseased kidneys. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2002;11:73–80. - PubMed
-
- Bidani AK, Griffin KA. Pathophysiology of hypertensive renal damage: implications for therapy. Hypertension. 2004;44:595–601. - PubMed
-
- Nadar S, Blann AD, Lip GY. Antihypertensive therapy and endothelial function. Curr Pharm Des. 2004;10:3607–3614. - PubMed
-
- Nadar SK, Tayebjee MH, Messerli F, Lip GY. Target organ damage in hypertension: pathophysiology and implications for drug therapy. Curr Pharm Des. 2006;12:1581–1592. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

