In-Cell RNA Hydrolysis Assay: A Method for the Determination of the RNase Activity of Potential RNases
- PMID: 25632893
- PMCID: PMC4432088
- DOI: 10.1007/s12033-015-9844-7
In-Cell RNA Hydrolysis Assay: A Method for the Determination of the RNase Activity of Potential RNases
Abstract
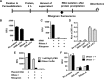
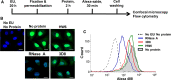
Conventional procedures to assay RNA degradation by a protein with ribonuclease (RNase) activity require a step to isolate intact RNA molecules, which are used as a substrate. Here, we established a novel "In-cell RNA hydrolysis assay" in which RNAs within cells are used as a substrate for the RNA-hydrolyzing protein, thereby avoiding the need to prepare intact RNA molecules. In this method, the degree of RNA degradation is indicated by the fluorescence intensity of RNA molecules released from fixed and permeabilized cells following treatment with the potential RNase. A catalytic 3D8 antibody capable of degrading RNAs and pancreatic RNase A were used as model RNases. Our data demonstrate that the novel In-cell RNA hydrolysis assay is a reliable and sensitive method to analyze the activities of potential RNA-hydrolyzing proteins such as catalytic antibodies.
Figures


Similar articles
-
A general ribonuclease assay using methylene blue.Anal Biochem. 1996 Aug 15;240(1):24-8. doi: 10.1006/abio.1996.0326. Anal Biochem. 1996. PMID: 8811875
-
How to Win the Battle with RNase.Cold Spring Harb Protoc. 2019 Feb 1;2019(2). doi: 10.1101/pdb.top101857. Cold Spring Harb Protoc. 2019. PMID: 30710029
-
An RNA-hydrolyzing recombinant antibody exhibits an antiviral activity against classical swine fever virus.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2010 May 14;395(4):484-9. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2010.04.032. Epub 2010 Apr 9. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2010. PMID: 20382124
-
Artificial ribonucleases.Adv Inorg Biochem. 1994;9:41-74. Adv Inorg Biochem. 1994. PMID: 7511321 Review.
-
Biological Activities of Secretory RNases: Focus on Their Oligomerization to Design Antitumor Drugs.Front Immunol. 2019 Nov 26;10:2626. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.02626. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31849926 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Williamson RA, Burgoon MP, Owens GP, Ghausi O, Leclerc E, Firme L, Carlson S, Corboy J, Parren PW, Sanna PP, Gilden DH, Burton DR. Anti-DNA antibodies are a major component of the intrathecal B cell response in multiple sclerosis. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 2001;98:1793–1798. doi: 10.1073/pnas.98.4.1793. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Parkhomenko TA, Legostaeva GA, Doronin BM, Buneva VN, Nevinsky GA. IgGs containing light chains of the lambda and kappa type and of all subclasses (IgG1–IgG4) from sera of patients with multiple sclerosis hydrolyze DNA. Journal of Molecular Recognition. 2010;23:486–494. doi: 10.1002/jmr.1016. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

