TOX3 is expressed in mammary ER(+) epithelial cells and regulates ER target genes in luminal breast cancer
- PMID: 25632947
- PMCID: PMC4324787
- DOI: 10.1186/s12885-015-1018-2
TOX3 is expressed in mammary ER(+) epithelial cells and regulates ER target genes in luminal breast cancer
Abstract
Background: A breast cancer susceptibility locus has been mapped to the gene encoding TOX3. Little is known regarding the expression pattern or biological role of TOX3 in breast cancer or in the mammary gland. Here we analyzed TOX3 expression in murine and human mammary glands and in molecular subtypes of breast cancer, and assessed its ability to alter the biology of breast cancer cells.
Methods: We used a cell sorting strategy, followed by quantitative real-time PCR, to study TOX3 gene expression in the mouse mammary gland. To study the expression of this nuclear protein in human mammary glands and breast tumors, we generated a rabbit monoclonal antibody specific for human TOX3. In vitro studies were performed on MCF7, BT474 and MDA-MB-231 cell lines to study the effects of TOX3 modulation on gene expression in the context of breast cancer cells.
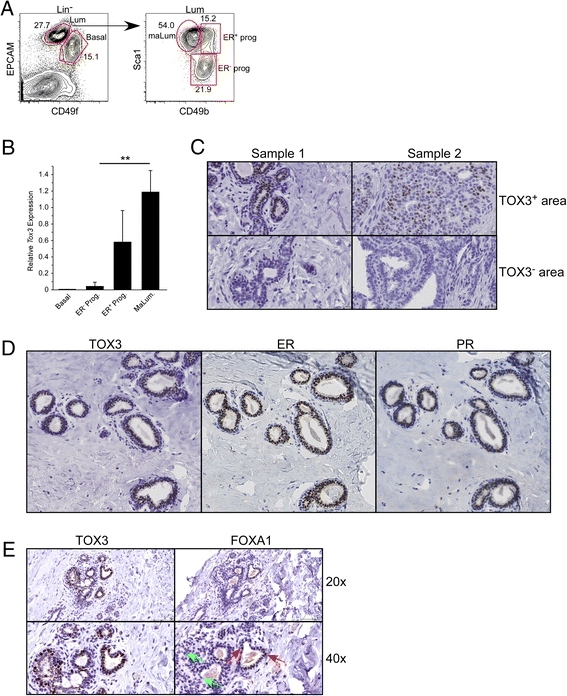
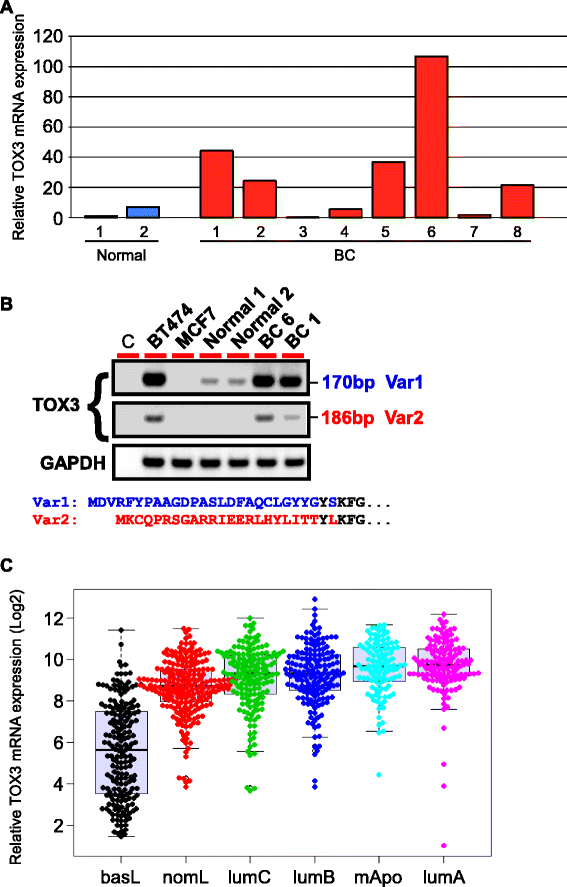
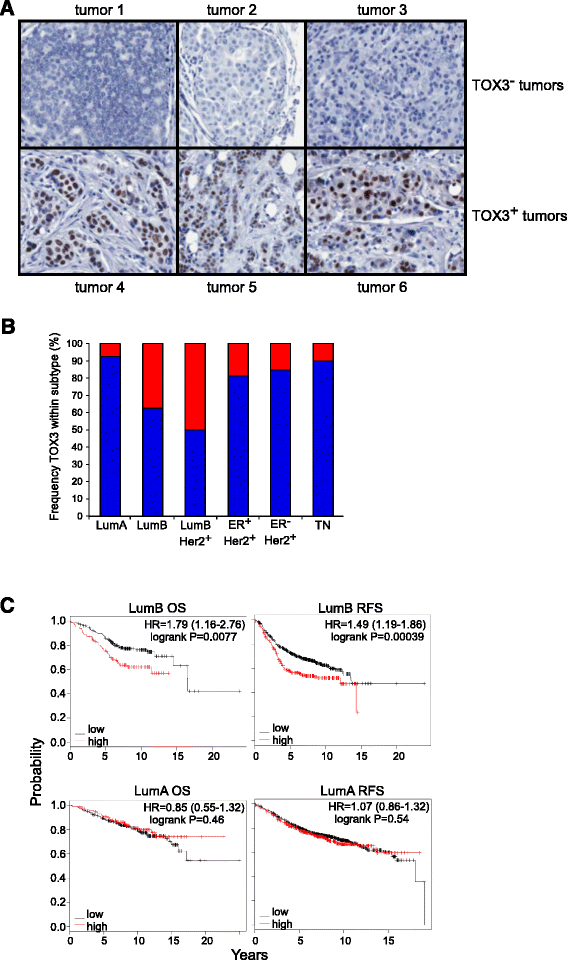
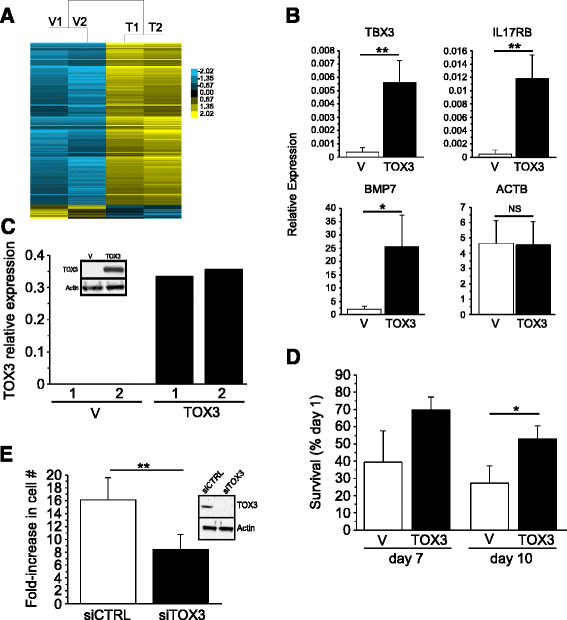
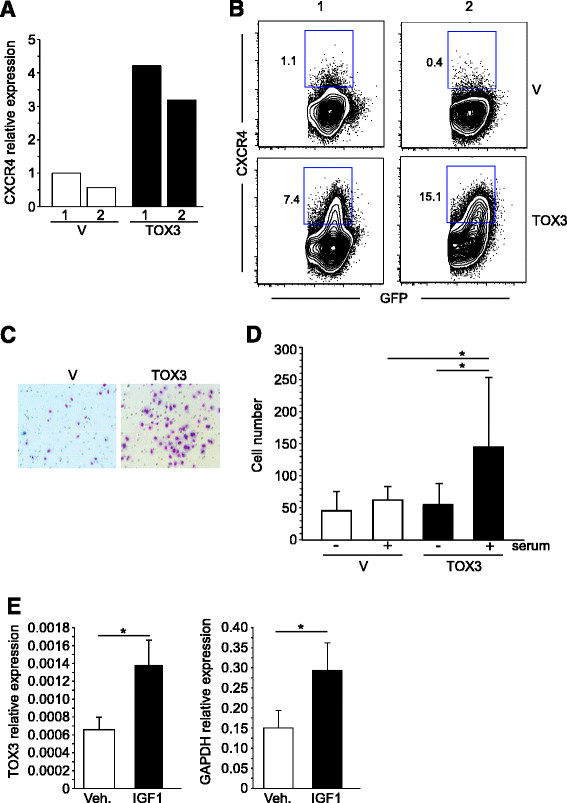
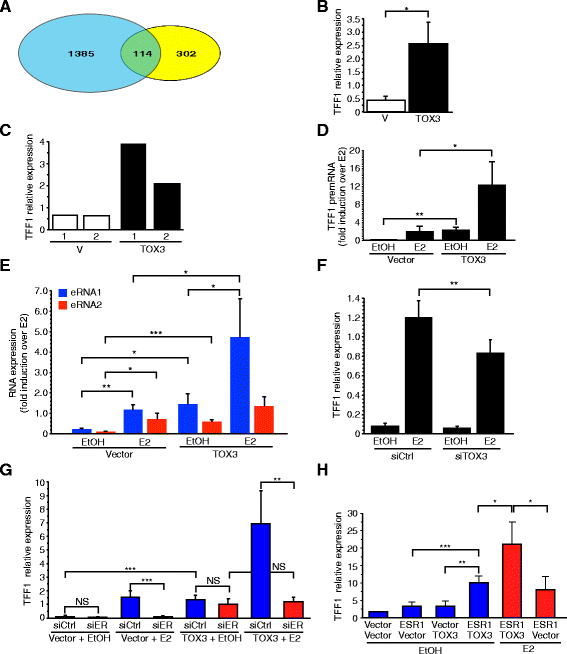
Results: We found TOX3 expression in estrogen receptor-positive mammary epithelial cells, including progenitor cells. A subset of breast tumors also highly expresses TOX3, with poor outcome associated with high expression of TOX3 in luminal B breast cancers. We also demonstrate the ability of TOX3 to alter gene expression in MCF7 luminal breast cancer cells, including cancer relevant genes TFF1 and CXCR4. Knockdown of TOX3 in a luminal B breast cancer cell line that highly expresses TOX3 is associated with slower growth. Surprisingly, TOX3 is also shown to regulate TFF1 in an estrogen-independent and tamoxifen-insensitive manner.
Conclusions: These results demonstrate that high expression of this protein likely plays a crucial role in breast cancer progression. This is in sharp contrast to previous studies that indicated breast cancer susceptibility is associated with lower expression of TOX3. Together, these results suggest two different roles for TOX3, one in the initiation of breast cancer, potentially related to expression of TOX3 in mammary epithelial cell progenitors, and another role for this nuclear protein in the progression of cancer. In addition, these results can begin to shed light on the reported association of TOX3 expression and breast cancer metastasis to the bone, and point to TOX3 as a novel regulator of estrogen receptor-mediated gene expression.
Figures
Similar articles
-
STAT1-deficient mice spontaneously develop estrogen receptor α-positive luminal mammary carcinomas.Breast Cancer Res. 2012 Jan 20;14(1):R16. doi: 10.1186/bcr3100. Breast Cancer Res. 2012. PMID: 22264274 Free PMC article.
-
Tip30 controls differentiation of murine mammary luminal progenitor to estrogen receptor-positive luminal cell through regulating FoxA1 expression.Cell Death Dis. 2014 May 22;5(5):e1242. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2014.224. Cell Death Dis. 2014. PMID: 24853420 Free PMC article.
-
ADA3 regulates normal and tumor mammary epithelial cell proliferation through c-MYC.Breast Cancer Res. 2016 Nov 16;18(1):113. doi: 10.1186/s13058-016-0770-9. Breast Cancer Res. 2016. PMID: 27852327 Free PMC article.
-
The hyperplastic phenotype in PR-A and PR-B transgenic mice: lessons on the role of estrogen and progesterone receptors in the mouse mammary gland and breast cancer.Vitam Horm. 2013;93:185-201. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-416673-8.00012-5. Vitam Horm. 2013. PMID: 23810007 Review.
-
Mechanisms of Regulation of Cell Fate in Breast Development and Cancer.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2025;1464:167-184. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-70875-6_10. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2025. PMID: 39821026 Review.
Cited by
-
Understanding genetic variations associated with familial breast cancer.World J Surg Oncol. 2024 Oct 10;22(1):271. doi: 10.1186/s12957-024-03553-9. World J Surg Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39390525 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Differential gene expression of tumor-infiltrating CD4+ T cells in advanced versus early stage colorectal cancer and identification of a gene signature of poor prognosis.Oncoimmunology. 2020 Sep 30;9(1):1825178. doi: 10.1080/2162402X.2020.1825178. Oncoimmunology. 2020. PMID: 33101776 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of novel gene expression signature in lung adenocarcinoma by using next-generation sequencing data and bioinformatics analysis.Oncotarget. 2017 Sep 18;8(62):104831-104854. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.21022. eCollection 2017 Dec 1. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 29285217 Free PMC article.
-
Novel Insights Into the Causal Effects and Shared Genetics Between Body Fat and Parkinson Disease.CNS Neurosci Ther. 2024 Nov;30(11):e70132. doi: 10.1111/cns.70132. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2024. PMID: 39578713 Free PMC article.
-
TOX3 is a favorable prognostic indicator and potential immunomodulatory factor in lung adenocarcinoma.Oncol Lett. 2019 Oct;18(4):4144-4152. doi: 10.3892/ol.2019.10748. Epub 2019 Aug 16. Oncol Lett. 2019. PMID: 31516613 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

