In vitro selection of single-stranded DNA molecular recognition elements against S. aureus alpha toxin and sensitive detection in human serum
- PMID: 25633102
- PMCID: PMC4346865
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms16022794
In vitro selection of single-stranded DNA molecular recognition elements against S. aureus alpha toxin and sensitive detection in human serum
Abstract
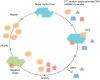
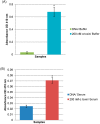
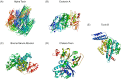
Alpha toxin is one of the major virulence factors secreted by Staphylococcus aureus, a bacterium that is responsible for a wide variety of infections in both community and hospital settings. Due to the prevalence of S. aureus related infections and the emergence of methicillin-resistant S. aureus, rapid and accurate diagnosis of S. aureus infections is crucial in benefiting patient health outcomes. In this study, a rigorous Systematic Evolution of Ligands by Exponential Enrichment (SELEX) variant previously developed by our laboratory was utilized to select a single-stranded DNA molecular recognition element (MRE) targeting alpha toxin with high affinity and specificity. At the end of the 12-round selection, the selected MRE had an equilibrium dissociation constant (Kd) of 93.7 ± 7.0 nM. Additionally, a modified sandwich enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) was developed by using the selected ssDNA MRE as the toxin-capturing element and a sensitive detection of 200 nM alpha toxin in undiluted human serum samples was achieved.
Figures

References
-
- Mediavilla J.R., Chen L., Uhlemann A.C., Hanson B.M., Rosenthal M., Stanak K., Koll B., Fries B.C., Armellino D., Schilling M.E., et al. Methicillin-susceptible Staphylococcus aureus ST398, New York and New Jersey, USA. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2012;18:700–702. doi: 10.3201/eid1804.111419. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Vandenesch F., Naimi T., Enright M.C., Lina G., Nimmo G.R., Heffernan H., Liassine N., Bes M., Greenland T., Reverdy M.E., Etienne J. Community-acquired methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus carrying Panton-Valentine leukocidin genes: Worldwide emergence. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2003;9:978–984. doi: 10.3201/eid0908.030089. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Moet G.J., Jones R.N., Biedenbach D.J., Stilwell M.G., Fritsche T.R. Contemporary causes of skin and soft tissue infections in North America, Latin America, and Europe: Report from the SENTRY Antimicrobial Surveillance Program (1998–2004) Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2007;57:7–13. doi: 10.1016/j.diagmicrobio.2006.05.009. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

