DRAM1 regulates apoptosis through increasing protein levels and lysosomal localization of BAX
- PMID: 25633293
- PMCID: PMC4669745
- DOI: 10.1038/cddis.2014.546
DRAM1 regulates apoptosis through increasing protein levels and lysosomal localization of BAX
Abstract
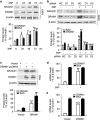
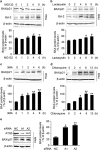
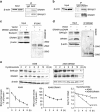
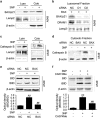
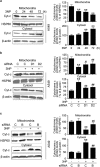
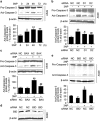
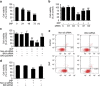
DRAM1 (DNA damage-regulated autophagy modulator 1) is a TP53 target gene that modulates autophagy and apoptosis. We previously found that DRAM1 increased autophagy flux by promoting lysosomal acidification and protease activation. However, the molecular mechanisms by which DRAM1 regulates apoptosis are not clearly defined. Here we report a novel pathway by which DRAM1 regulates apoptosis involving BAX and lysosomes. A549 or HeLa cells were treated with the mitochondrial complex II inhibitor, 3-nitropropionic acid (3NP), or an anticancer drug, doxorubicin. Changes in the protein and mRNA levels of BAX and DRAM1 and the role of DRAM1 in BAX induction were determined. The interaction between DRAM1 and BAX and its effect on BAX degradation, BAX lysosomal localization, the release of cathepsin B and cytochrome c by BAX and the role of BAX in 3NP- or doxorubicin-induced cell death were studied. The results showed that BAX, a proapoptotic protein, was induced by DRAM1 in a transcription-independent manner. BAX was degraded by autophagy under basal conditions; however, its degradation was inhibited when DRAM1 expression was induced. There was a protein interaction between DRAM1 and BAX and this interaction prolonged the half-life of BAX. Furthermore, upregulated DRAM1 recruited BAX to lysosomes, leading to the release of lysosomal cathepsin B and cleavage of BID (BH3-interacting domain death agonist). BAX mediated the release of mitochondrial cytochrome c, activation of caspase-3 and cell death partially through the lysosome-cathepsin B-tBid pathway. These results indicate that DRAM1 regulates apoptosis by inhibiting BAX degradation. In addition to mitochondria, lysosomes may also be involved in BAX-initiated apoptosis.
Figures

References
-
- Pattingre S, Tassa A, Qu X, Garuti R, Liang XH, Mizushima N et al. Bcl-2 antiapoptotic proteins inhibit Beclin 1-dependent autophagy. Cell 2005; 122: 927–939. - PubMed
-
- Crighton D, Wilkinson S, Ryan KM. DRAM links autophagy to p53 and programmed cell death. Autophagy 2007; 3: 72–74. - PubMed
-
- Crighton D, Wilkinson S, O'Prey J, Syed N, Smith P, Harrison PR et al. DRAM, a p53-induced modulator of autophagy, is critical for apoptosis. Cell 2006; 126: 121–134. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

