Evaluation of the radiolabeled boronic acid-based FAP inhibitor MIP-1232 for atherosclerotic plaque imaging
- PMID: 25633335
- PMCID: PMC6272135
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules20022081
Evaluation of the radiolabeled boronic acid-based FAP inhibitor MIP-1232 for atherosclerotic plaque imaging
Abstract
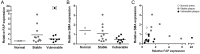
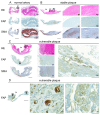
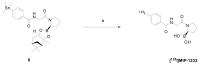
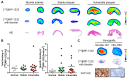
Research towards the non-invasive imaging of atherosclerotic plaques is of high clinical priority as early recognition of vulnerable plaques may reduce the incidence of cardiovascular events. The fibroblast activation protein alpha (FAP) was recently proposed as inflammation-induced protease involved in the process of plaque vulnerability. In this study, FAP mRNA and protein levels were investigated by quantitative polymerase chain reaction and immunohistochemistry, respectively, in human endarterectomized carotid plaques. A published boronic-acid based FAP inhibitor, MIP-1232, was synthetized and radiolabeled with iodine-125. The potential of this radiotracer to image plaques was evaluated by in vitro autoradiography with human carotid plaques. Specificity was assessed with a xenograft with high and one with low FAP level, grown in mice. Target expression analyses revealed a moderately higher protein level in atherosclerotic plaques than normal arteries correlating with plaque vulnerability. No difference in expression was determined on mRNA level. The radiotracer was successfully produced and accumulated strongly in the FAP-positive SK-Mel-187 melanoma xenograft in vitro while accumulation was negligible in an NCI-H69 xenograft with low FAP levels. Binding of the tracer to endarterectomized tissue was similar in plaques and normal arteries, hampering its use for atherosclerosis imaging.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Ylä-Herttuala S., Bentzon J.F., Daemen M., Falk E., Garcia-Garcia H.M., Herrmann J., Hoefer I., Jukema J.W., Krams R., Kwak B.R., et al. Stabilisation of atherosclerotic plaques. Position paper of the european society of cardiology (ESC) working group on atherosclerosis and vascular biology. Thromb. Haemost. 2011;106:1–19. doi: 10.1160/TH10-12-0784. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Van der Wal A.C., Becker A.E., van der Loos C.M., Das P.K. Site of intimal rupture or erosion of thrombosed coronary atherosclerotic plaques is characterized by an inflammatory process irrespective of the dominant plaque morphology. Circulation. 1994;89:36–44. doi: 10.1161/01.CIR.89.1.36. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Galis Z.S., Khatri J.J. Matrix metalloproteinases in vascular remodeling and atherogenesis: The good, the bad, and the ugly. Circ. Res. 2002;90:251–262. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

