Oncogenes and tumor suppressor genes in squamous cell carcinoma of the tongue in young patients
- PMID: 25633809
- PMCID: PMC4413665
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.2850
Oncogenes and tumor suppressor genes in squamous cell carcinoma of the tongue in young patients
Abstract
Objectives: The occurrence of squamous cell carcinoma of the tongue (SCCT) of young patients increased. There are still controversies about patient prognosis. The underlying molecular mechanisms remain unclear.
Methods: 276 patients (66 ≤45, 210 >45 years) with SCCT were included. Clinical parameters and survival data were assessed. Oncogenes and tumor suppressors were analyzed via immunohistochemistry (p53, CXCR4, p16, EGFR) and qPCR (CDK4, CDKN2A, TP53, MDM2, AKT1, PIK3CA, NRAS, HRAS, KRAS, HGF, MET, EGF, ATM, BRCA1, E2F1, FHIT, RUNX3, STK11, BCL2, CTNNB1).
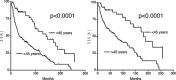
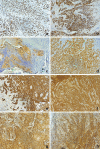
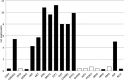
Results: The median overall survival was 142 (≤45 years) and 34 months (>45 years) (p < 0.0001; HR [95%CI]: 0.37 [0.30-0.58]). Disease specific survival in patients ≤45 years was with 181 months significantly higher than in patients >45 years (p < 0.0001; HR [95%CI]: 0.33 [0.26-0.57]). Immunhistochemistry visualized a comparable expression of analyzed proteins. QPCR demonstrated in patients ≤45 years a higher expression of genes that are associated with carcinogenesis (CTNNB1, STK11, CDKN2A, HGF, MET) as well as tumor suppressors that constitute an enhanced radio-sensitivity (ATM, BRCA1E2F1, FHIT).
Conclusion: Derogation of the WNT-CTNNB1-STK11 and CDKN2A-HGF-MET pathway can constitute the carcinogenesis, while the higher expression of radio-sensitizers ATM, BRCA1E2F1 and FHIT can explain the better OS/DSS in young patients.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors sate no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Parkin DM, Bray F, Ferlay J, Pisani P. Global cancer statistics, 2002. CA Cancer J Clin. 2005;55:74–108. - PubMed
-
- Fuller CD, Wang SJ, Thomas CR, Jr, Hoffman HT, Weber RS, Rosenthal DI. Conditional survival in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: results from the SEER dataset 1973–1998. Cancer. 2007;109:1331–1343. - PubMed
-
- Chaturvedi AK, Engels EA, Anderson WF, Gillison ML. Incidence trends for human papillomavirus-related and -unrelated oral squamous cell carcinomas in the United States. J Clin Oncol. 2008;26:612–619. - PubMed
-
- Golas SM. Trends in palatine tonsillar cancer incidence and mortality rates in the United States. Community Dent Oral Epidemiol. 2007;35:98–108. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

