Organochlorine insecticides induce NADPH oxidase-dependent reactive oxygen species in human monocytic cells via phospholipase A2/arachidonic acid
- PMID: 25633958
- PMCID: PMC4684262
- DOI: 10.1021/tx500323h
Organochlorine insecticides induce NADPH oxidase-dependent reactive oxygen species in human monocytic cells via phospholipase A2/arachidonic acid
Abstract
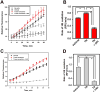
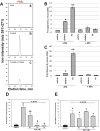
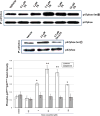
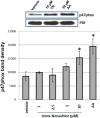
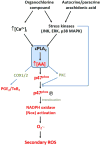
Bioaccumulative organohalogen chemicals, such as organochlorine (OC) insecticides, have been increasingly associated with disease etiology; however, the mechanistic link between chemical exposure and diseases, such as atherosclerosis, cancer, and diabetes, is complex and poorly defined. Systemic oxidative stress stemming from OC exposure might play a vital role in the development of these pathologies. Monocytes are important surveillance cells of the innate immune system that respond to extracellular signals possessing danger-associated molecular patterns by synthesizing oxyradicals, such as superoxide, for the purpose of combating infectious pathogens. We hypothesized that OC chemicals can be toxic to monocytes because of an inappropriate elevation in superoxide-derived reactive oxygen species (ROS) capable of causing cellular oxidative damage. Reactive oxyradicals are generated in monocytes in large part by NADPH oxidase (Nox). The present study was conducted to examine the ability of two chlorinated cyclodiene compounds, trans-nonachlor and dieldrin, as well as p,p'-DDE, a chlorinated alicyclic metabolite of DDT, to stimulate Nox activity in a human monocytic cell line and to elucidate the mechanisms for this activation. Human THP-1 monocytes treated with either trans-nonachlor or dieldrin (0.1-10 μM in the culture medium) exhibited elevated levels of intracellular ROS, as evidenced by complementary methods, including flow cytometry analysis using the probe DCFH-DA and hydroethidine-based fluorometric and UPLC-MS assays. In addition, the induced reactive oxygen flux caused by trans-nonachlor was also observed in two other cell lines, murine J774 macrophages and human HL-60 cells. The central role of Nox in OC-mediated oxidative stress was demonstrated by the attenuated superoxide production in OC-exposed monocytes treated with the Nox inhibitors diphenyleneiodonium and VAS-2870. Moreover, monocytes challenged with OCs exhibited increased phospho-p47(phox) levels and enhanced p47(phox) membrane localization compared to that in vehicle-treated cells. p47(phox) is a cytosolic regulatory subunit of Nox, and its phosphorylation and translocation to the NOX2 catalytic subunit in membranes is a requisite step for Nox assembly and activation. Dieldrin and trans-nonachlor treatments of monocytes also resulted in marked increases in arachidonic acid (AA) and eicosanoid production, which could be abrogated by the phospholipase A2 (PLA2) inhibitor arachidonoyltrifluoromethyl ketone (ATK) but not by calcium-independent PLA2 inhibitor bromoenol lactone. This suggested that cytosolic PLA2 plays a crucial role in the induction of Nox activity by increasing the intracellular pool of AA that activates protein kinase C, which phosphorylates p47(phox). In addition, ATK also blocked OC-induced p47(phox) serine phosphorylation and attenuated ROS levels, which further supports the notion that the AA pool liberated by cytosolic PLA2 is responsible for Nox activation. Together, the results suggest that trans-nonachlor and dieldrin are capable of increasing intracellular superoxide levels via a Nox-dependent mechanism that relies on elevated intracellular AA levels. These findings are significant because chronic activation of monocytes by environmental toxicants might contribute to pathogenic oxidative stress and inflammation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures


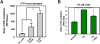



Similar articles
-
Cytosolic phospholipase A2 (cPLA2) regulation of human monocyte NADPH oxidase activity. cPLA2 affects translocation but not phosphorylation of p67(phox) and p47(phox).J Biol Chem. 2002 Jul 12;277(28):25385-92. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M203630200. Epub 2002 May 6. J Biol Chem. 2002. PMID: 12101222
-
Oxyradical stress increases the biosynthesis of 2-arachidonoylglycerol: involvement of NADPH oxidase.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2016 Dec 1;311(6):C960-C974. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00251.2015. Epub 2016 Oct 26. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2016. PMID: 27784678 Free PMC article.
-
Kaempferol suppresses collagen-induced platelet activation by inhibiting NADPH oxidase and protecting SHP-2 from oxidative inactivation.Free Radic Biol Med. 2015 Jun;83:41-53. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2015.01.018. Epub 2015 Jan 31. Free Radic Biol Med. 2015. PMID: 25645952
-
Arachidonic Acid and Nitroarachidonic: Effects on NADPH Oxidase Activity.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2019;1127:85-95. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-11488-6_6. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2019. PMID: 31140173 Review.
-
The effect of reactive oxygen species on the synthesis of prostanoids from arachidonic acid.J Physiol Pharmacol. 2013 Aug;64(4):409-21. J Physiol Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 24101387 Review.
Cited by
-
Children's white blood cell counts in relation to developmental exposures to methylmercury and persistent organic pollutants.Reprod Toxicol. 2017 Mar;68:207-214. doi: 10.1016/j.reprotox.2016.08.001. Epub 2016 Aug 4. Reprod Toxicol. 2017. PMID: 27497749 Free PMC article.
-
The association of serum trans-nonachlor levels with atherosclerosis.J Toxicol Environ Health A. 2016;79(5):210-20. doi: 10.1080/15287394.2016.1143901. Epub 2016 Mar 8. J Toxicol Environ Health A. 2016. PMID: 26953872 Free PMC article.
-
Insecticide use and risk of non-Hodgkin lymphoma subtypes: A subset meta-analysis of the North American Pooled Project.Int J Cancer. 2020 Dec 15;147(12):3370-3383. doi: 10.1002/ijc.33164. Epub 2020 Jul 31. Int J Cancer. 2020. PMID: 32574374 Free PMC article.
-
CES1 Releases Oxylipins from Oxidized Triacylglycerol (oxTAG) and Regulates Macrophage oxTAG/TAG Accumulation and PGE2/IL-1β Production.ACS Chem Biol. 2023 Jul 21;18(7):1564-1581. doi: 10.1021/acschembio.3c00194. Epub 2023 Jun 22. ACS Chem Biol. 2023. PMID: 37348046 Free PMC article.
-
The ROS-FOXO pathway mediates broad-spectrum detoxification of acaricides in Tetranychus cinnabarinus.Commun Biol. 2025 Aug 23;8(1):1274. doi: 10.1038/s42003-025-08726-0. Commun Biol. 2025. PMID: 40849604 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Min JY, Cho JS, Lee KJ, Park JB, Park SG, Kim JY, Min KB. Potential role for organochlorine pesticides in the prevalence of peripheral arterial diseases in obese persons: results from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 1999–2004. Atherosclerosis. 2011;218:200–206. - PubMed
-
- Alavanja MC, Ross MK, Bonner MR. Increased cancer burden among pesticide applicators and others due to pesticide exposure. CA–Cancer J Clin. 2013;63:120–142. - PubMed
-
- Kumar J, Monica Lind P, Salihovic S, van Bavel B, Lind L, Ingelsson E. Influence of persistent organic pollutants on oxidative stress in population-based samples. Chemosphere. 2014;114:303–309. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

