Cardiac protective effects of dexrazoxane on animal cardiotoxicity model induced by anthracycline combined with trastuzumab is associated with upregulation of calpain-2
- PMID: 25634181
- PMCID: PMC4602968
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000000445
Cardiac protective effects of dexrazoxane on animal cardiotoxicity model induced by anthracycline combined with trastuzumab is associated with upregulation of calpain-2
Abstract
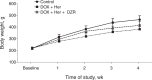
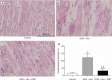
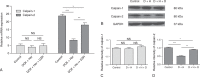
Cardiotoxicity is a well-recognized side effect induced by chemotherapeutic drugs such as anthracycline and trastuzumab through different mechanisms. Currently, accumulating evidence supports that dexrazoxane (DZR) can minimize the risk of cardiotoxicity. In this study, we investigated whether dexrzoxane could reduce cardiotoxicity in the treatment of anthracycline combined with trastuzumab. We randomly divided 90 experimental F344 rats into control group, chemotherapeutics and trastuzumab (doxorubicin [DOX] + herceptin [Her]) group, and chemotherapeutics, trastuzumab, and DZR (DOX + Her + DZR) group. Animal status and body weight, cardiac function, serum cardiac markers, cardiomyocyte apoptosis of the rats, and expression level of calpain-2 were evaluated. Left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) and fractional shortening (FS) of the left ventricle were observed. The serum levels of malondialdehyde (MDA) and cardiac troponin I (cTnI) and cardiomyocyte apoptosis were detected by enzyme linked immunosorbent assay and TdT-mediated dUTP nick end labeling assays. The mRNA and protein level of calpain-2 were measured by reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction and Western blot. We observed that the LVEF and FS of the left ventricle were significantly higher in the DOX + Her + DZR group than that in the DOX + Her group (P < 0.05). The serum levels of MDA and cTnI between DOX + Her group and DOX + Her + DZR group were significantly different. In addition, cardiomyocyte apoptosis in the DOX + Her + DZR group was significantly less severe than that in the DOX + Her group (P < 0.05). After DZR treatment, the calpain-2 mRNA and protein levels in the DOX + Her + DZR group were significantly higher than the DOX + Her group (P < 0.05). Our results suggest that DZR can effectively reduce the cardiotoxicity of combinatorial treatment of trastuzumab and anthracycline partly through upregulating calpain-2.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Protective Effects of Dexrazoxane against Doxorubicin-Induced Cardiotoxicity: A Metabolomic Study.PLoS One. 2017 Jan 10;12(1):e0169567. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0169567. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28072830 Free PMC article.
-
Humanin analog enhances the protective effect of dexrazoxane against doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2018 Sep 1;315(3):H634-H643. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00155.2018. Epub 2018 May 18. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2018. PMID: 29775411 Free PMC article.
-
Protection against doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity in weanling rats by dexrazoxane.Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 1999;43(2):151-6. doi: 10.1007/s002800050876. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 1999. PMID: 9923821
-
Nicotinic Acid Riboside Regulates Nrf-2/P62-Related Oxidative Stress and Autophagy to Attenuate Doxorubicin-Induced Cardiomyocyte Injury.Biomed Res Int. 2022 Feb 22;2022:6293329. doi: 10.1155/2022/6293329. eCollection 2022. Biomed Res Int. 2022. PMID: 35242876 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pharmaceutical Measures to Prevent Doxorubicin-Induced Cardiotoxicity.Mini Rev Med Chem. 2017;17(1):44-50. doi: 10.2174/1389557516666160621083659. Mini Rev Med Chem. 2017. PMID: 27337969 Review.
Cited by
-
Enhanced antitumor activity and attenuated cardiotoxicity of Epirubicin combined with Paeonol against breast cancer.Tumour Biol. 2016 Sep;37(9):12301-12313. doi: 10.1007/s13277-016-5088-9. Epub 2016 Jun 7. Tumour Biol. 2016. PMID: 27272157
-
Calpain-2 promotes MKP-1 expression protecting cardiomyocytes in both in vitro and in vivo mouse models of doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity.Arch Toxicol. 2019 Apr;93(4):1051-1065. doi: 10.1007/s00204-019-02405-w. Epub 2019 Feb 27. Arch Toxicol. 2019. PMID: 30810770 Free PMC article.
-
Myocardial protection of propofol on apoptosis induced by anthracycline by PI3K/AKT/Bcl-2 pathway in rats.Ann Transl Med. 2022 May;10(10):555. doi: 10.21037/atm-22-1549. Ann Transl Med. 2022. PMID: 35722399 Free PMC article.
-
Calpain research for drug discovery: challenges and potential.Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2016 Dec;15(12):854-876. doi: 10.1038/nrd.2016.212. Epub 2016 Nov 11. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2016. PMID: 27833121 Review.
-
Antioxidant Protection against Trastuzumab Cardiotoxicity in Breast Cancer Therapy.Antioxidants (Basel). 2023 Feb 10;12(2):457. doi: 10.3390/antiox12020457. Antioxidants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36830015 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Morris PG, Hudis CA. Trastuzumab-related cardiotoxicity following anthracycline-based adjuvant chemotherapy: how worried should we be? J Clin Oncol 2010; 28:3407–3410. - PubMed
-
- Thavendiranathan P, Poulin F, Lin KD, et al. Use of myocardial strain imaging by echocardiography for the early detection of cardiotoxicity in patients during and after cancer chemotherapy: a systematic review. J Am Coll Cardiol 2014; 63 (25 Pt A):2751–2768. - PubMed
-
- Goldhirsch A, Wood WC, Gelber RD, et al. Progress and promise: highlights of the international expert consensus on the primary therapy of early breast cancer 2007. Ann Oncol 2007; 18:1133–1144. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

