Quantitative analysis of receptor tyrosine kinase-effector coupling at functionally relevant stimulus levels
- PMID: 25635057
- PMCID: PMC4400318
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M114.602268
Quantitative analysis of receptor tyrosine kinase-effector coupling at functionally relevant stimulus levels
Abstract
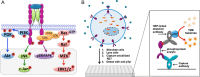
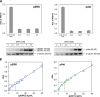
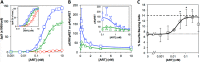
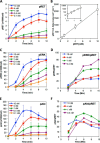
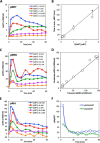
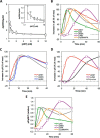
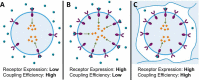
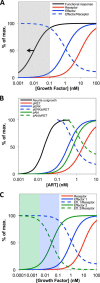
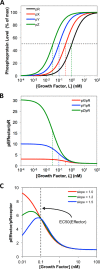
A major goal of current signaling research is to develop a quantitative understanding of how receptor activation is coupled to downstream signaling events and to functional cellular responses. Here, we measure how activation of the RET receptor tyrosine kinase on mouse neuroblastoma cells by the neurotrophin artemin (ART) is quantitatively coupled to key downstream effectors. We show that the efficiency of RET coupling to ERK and Akt depends strongly on ART concentration, and it is highest at the low (∼100 pM) ART levels required for neurite outgrowth. Quantitative discrimination between ERK and Akt pathway signaling similarly is highest at this low ART concentration. Stimulation of the cells with 100 pM ART activated RET at the rate of ∼10 molecules/cell/min, leading at 5-10 min to a transient peak of ∼150 phospho-ERK (pERK) molecules and ∼50 pAkt molecules per pRET, after which time the levels of these two signaling effectors fell by 25-50% while the pRET levels continued to slowly rise. Kinetic experiments showed that signaling effectors in different pathways respond to RET activation with different lag times, such that the balance of signal flux among the different pathways evolves over time. Our results illustrate that measurements using high, super-physiological growth factor levels can be misleading about quantitative features of receptor signaling. We propose a quantitative model describing how receptor-effector coupling efficiency links signal amplification to signal sensitization between receptor and effector, thereby providing insight into design principles underlying how receptors and their associated signaling machinery decode an extracellular signal to trigger a functional cellular outcome.
Keywords: Akt PKB; Artemin; Extracellular Signal-regulated Kinase (ERK); Kinetics; Mitogen-activated Protein Kinase (MAPK); Neurite Outgrowth; RET; Signal Gain; Signal Transduction; Systems Biology.
© 2015 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Dok-4 regulates GDNF-dependent neurite outgrowth through downstream activation of Rap1 and mitogen-activated protein kinase.J Cell Sci. 2006 Aug 1;119(Pt 15):3067-77. doi: 10.1242/jcs.03043. Epub 2006 Jul 4. J Cell Sci. 2006. PMID: 16820412
-
Characterization of intracellular signals via tyrosine 1062 in RET activated by glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor.Oncogene. 2000 Sep 14;19(39):4469-75. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1203799. Oncogene. 2000. PMID: 11002419
-
Ret oncogene signal transduction via a IRS-2/PI 3-kinase/PKB and a SHC/Grb-2 dependent pathway: possible implication for transforming activity in NIH3T3 cells.Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2000 Sep 25;167(1-2):69-76. doi: 10.1016/s0303-7207(00)00283-5. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2000. PMID: 11000521
-
Quantitative proteomic analyses of dynamic signalling events in cortical neurons undergoing excitotoxic cell death.Cell Death Dis. 2019 Mar 1;10(3):213. doi: 10.1038/s41419-019-1445-0. Cell Death Dis. 2019. PMID: 30824683 Free PMC article.
-
Rate thresholds in cell signaling have functional and phenotypic consequences in non-linear time-dependent environments.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023 Mar 21;11:1124874. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2023.1124874. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023. PMID: 37025183 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Counting growth factors in single cells with infrared quantum dots to measure discrete stimulation distributions.Nat Commun. 2019 Feb 22;10(1):909. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-08754-5. Nat Commun. 2019. PMID: 30796217 Free PMC article.
-
A high-density immunoblotting methodology for quantification of total protein levels and phosphorylation modifications.Sci Rep. 2015 Nov 23;5:16995. doi: 10.1038/srep16995. Sci Rep. 2015. PMID: 26592927 Free PMC article.
-
Crosstalk between protein kinases AKT and ERK1/2 in human lung tumor-derived cell models.Front Oncol. 2023 Jan 4;12:1045521. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.1045521. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 36686779 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Androulakis I. P., Kamisoglu K., Mattick J. S. (2013) Topology and dynamics of signaling networks: in search of transcriptional control of the inflammatory response. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 15, 1–28 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

