Electroencephalogram and magnetic resonance imaging comparison as a predicting factor for neurodevelopmental outcome in hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy infant treated with hypothermia
- PMID: 25635216
- PMCID: PMC4292060
- DOI: 10.4081/pr.2014.5532
Electroencephalogram and magnetic resonance imaging comparison as a predicting factor for neurodevelopmental outcome in hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy infant treated with hypothermia
Abstract
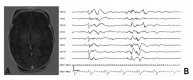
Hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy (HIE) is an important cause of acute neurological damage in newborns at (or near) term. Several trials in recent years have shown that moderate hypothermia by total body cooling or selective head is an effective intervention to reduce mortality and major disability in infants survived a perinatal hypoxic-ischemic attack. Follow-up in these patients is very important to establish neurodevelopmental outcome, and specific markers can lead us to detect predicting sign for good or poor outcome. We reported a few cases of newborn with HIE treated with hypothermia, in whom the comparison between electroencephalogram (EEG) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) represents the first marker for neurodevelopment outcome prediction. The continuous EEG monitoring showed a depressed EEG activity with diffuse burst depression in 7 patients. No epileptic abnormalities were registered. In 10 out of 20 patients no abnormalities of the background activity and no epileptic abnormalities were observed. We found that a depressed EEG activity during the first 72 h of life and a diffused alteration of basal ganglia at MRI were correlated with a poor neurodevelopmental outcome at 18 months of follow-up.
Keywords: electroencephalogram monitoring; hypothermia; long term; magnetic resonance imaging; neonates.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interests: the authors declare no potential conflict of interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Therapeutic hypothermia for neonatal hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy: magnetic resonance imaging findings and neurological outcomes in a Brazilian cohort.J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2019 Aug;32(16):2727-2734. doi: 10.1080/14767058.2018.1448773. Epub 2018 Mar 13. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2019. PMID: 29504433
-
A Systematic Review of EEG and MRI Features for Predicting Long-Term Neurological Outcomes in Cooled Neonates With Hypoxic-Ischemic Encephalopathy (HIE).Cureus. 2024 Oct 14;16(10):e71431. doi: 10.7759/cureus.71431. eCollection 2024 Oct. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 39539899 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Correlation of EEG, CT, and MRI Brain with Neurological Outcome at 12 Months in Term Newborns with Hypoxic Ischemic Encephalopathy.J Clin Neonatol. 2013 Jul;2(3):125-30. doi: 10.4103/2249-4847.119996. J Clin Neonatol. 2013. PMID: 24251256 Free PMC article.
-
Selective Head versus Whole Body Cooling Treatment of Hypoxic-Ischemic Encephalopathy: Comparison of Electroencephalogram and Magnetic Resonance Imaging Findings.Am J Perinatol. 2020 Oct;37(12):1264-1270. doi: 10.1055/s-0039-1693466. Epub 2019 Jul 25. Am J Perinatol. 2020. PMID: 31344712
-
Hypothermia therapy for newborns with hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy.J Pediatr (Rio J). 2015 Nov-Dec;91(6 Suppl 1):S78-83. doi: 10.1016/j.jped.2015.07.004. Epub 2015 Sep 4. J Pediatr (Rio J). 2015. PMID: 26354871 Review.
Cited by
-
Prognostic Value of Clinical Tests in Neonates With Hypoxic-Ischemic Encephalopathy Treated With Therapeutic Hypothermia: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Front Neurol. 2020 Feb 25;11:133. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2020.00133. eCollection 2020. Front Neurol. 2020. PMID: 32161566 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Shankaran S, Laptook AR, Ehrenkranz RA, et al. Whole body hypothermia for neonates with hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy. N Engl J Med 2005;353: 1574-84. - PubMed
-
- Azzopardi D, Strohm B, Edwards AD, et al. Moderate hypothermia to treat perinatal asphyxial encephalopathy. N Engl J Med 2009;361:1349-58. - PubMed
-
- Walsh BH, Murrray DM, Boylan GB.The use of conventional EEG for the assessment of hypoxic ischaemic encephalopathy in the newborn: a review. Clin Neurophysiol 2011;122:1284-94 - PubMed
-
- Mariani E, Scelsa B, Pogliani L, et al. Prognostic value of electroencephalograms in asphyxiated newborns treated with hypothermia. Pediatr Neurol 2008;39:317-24. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources