Baseline magnetic resonance imaging of the optic nerve provides limited predictive information on short-term recovery after acute optic neuritis
- PMID: 25635863
- PMCID: PMC4312052
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0113961
Baseline magnetic resonance imaging of the optic nerve provides limited predictive information on short-term recovery after acute optic neuritis
Abstract
Background: In acute optic neuritis, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) may help to confirm the diagnosis as well as to exclude alternative diagnoses. Yet, little is known on the value of optic nerve imaging for predicting clinical symptoms or therapeutic outcome.
Purpose: To evaluate the benefit of optic nerve MRI for predicting response to appropriate therapy and recovery of visual acuity.
Methods: Clinical data as well as visual evoked potentials (VEP) and MRI results of 104 patients, who were treated at the Department of Neurology with clinically definite optic neuritis between December 2010 and September 2012 were retrospectively reviewed including a follow up within 14 days.
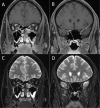
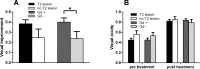
Results: Both length of the Gd enhancing lesion (r = -0.38; p = 0.001) and the T2 lesion (r = -0.25; p = 0.03) of the optic nerve in acute optic neuritis showed a medium correlation with visual acuity after treatment. Although visual acuity pre-treatment was little but nonsignificantly lower if Gd enhancement of the optic nerve was detected via orbital MRI, improvement of visual acuity after adequate therapy was significantly better (0.40 vs. 0.24; p = 0.04). Intraorbitally located Gd enhancing lesions were associated with worse visual improvement compared to canalicular, intracranial and chiasmal lesions (0.35 vs. 0.54; p = 0.02).
Conclusion: Orbital MRI is a broadly available, valuable tool for predicting the improvement of visual function. While the accurate individual prediction of long-term outcomes after appropriate therapy still remains difficult, lesion length of Gd enhancement and T2 lesion contribute to its prediction and a better short-term visual outcome may be associated with detection and localization of Gd enhancement along the optic nerve.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
MRI of acute optic neuritis (ON) at the first episode: Can we predict the visual outcome and the development of multiple sclerosis (MS)?Radiol Med. 2019 Dec;124(12):1296-1303. doi: 10.1007/s11547-019-01073-1. Epub 2019 Aug 21. Radiol Med. 2019. PMID: 31435862
-
Optic neuritis: correlation of pain and magnetic resonance imaging.Ophthalmology. 2003 Aug;110(8):1646-9. doi: 10.1016/S0161-6420(03)00477-9. Ophthalmology. 2003. PMID: 12917187
-
Radiologic Predictors of Visual Outcome in Myelin Oligodendrocyte Glycoprotein-Related Optic Neuritis.Ophthalmology. 2025 Feb;132(2):170-180. doi: 10.1016/j.ophtha.2024.08.018. Epub 2024 Aug 14. Ophthalmology. 2025. PMID: 39151754
-
[Past, present, and future in Leber's hereditary optic neuropathy].Nippon Ganka Gakkai Zasshi. 2001 Dec;105(12):809-27. Nippon Ganka Gakkai Zasshi. 2001. PMID: 11802455 Review. Japanese.
-
Systemic lupus erythematosus-associated optic neuritis: clinical experience and literature review.Acta Ophthalmol. 2009 Mar;87(2):204-10. doi: 10.1111/j.1755-3768.2008.01193.x. Epub 2008 May 27. Acta Ophthalmol. 2009. PMID: 18507726 Review.
Cited by
-
Clinical characteristics depending on magnetic resonance imaging patterns in idiopathic isolated optic neuritis.Sci Rep. 2023 Feb 4;13(1):2053. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-28904-6. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 36739455 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of clinical history on MRI interpretation of optic neuropathy.Heliyon. 2016 Sep 16;2(9):e00162. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2016.e00162. eCollection 2016 Sep. Heliyon. 2016. PMID: 27699283 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of the initial orbital MRI in aquaporin-4 antibody-positive optic neuritis (AQP4-ON): lesion location and lesion length can be predictive of visual prognosis.Neuroradiology. 2024 Jun;66(6):897-906. doi: 10.1007/s00234-024-03306-1. Epub 2024 Feb 15. Neuroradiology. 2024. PMID: 38358511
-
Radiomic analysis of the optic nerve at the first episode of acute optic neuritis: an indicator of optic nerve pathology and a predictor of visual recovery?Radiol Med. 2021 May;126(5):698-706. doi: 10.1007/s11547-020-01318-4. Epub 2021 Jan 3. Radiol Med. 2021. PMID: 33392980
-
MRI of acute optic neuritis (ON) at the first episode: Can we predict the visual outcome and the development of multiple sclerosis (MS)?Radiol Med. 2019 Dec;124(12):1296-1303. doi: 10.1007/s11547-019-01073-1. Epub 2019 Aug 21. Radiol Med. 2019. PMID: 31435862
References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

