How much oxygen in adult cardiac arrest?
- PMID: 25636001
- PMCID: PMC4520204
- DOI: 10.1186/s13054-014-0555-4
How much oxygen in adult cardiac arrest?
Abstract
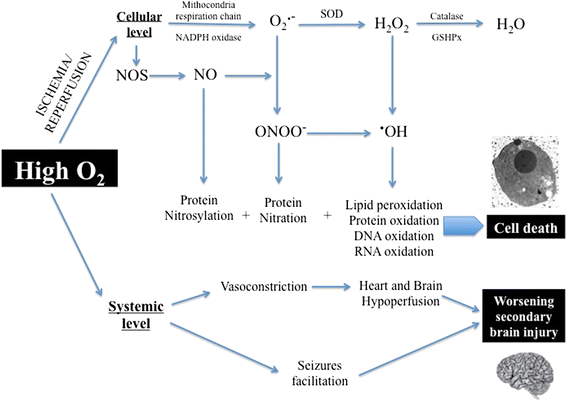
Although experimental studies have suggested that a high arterial oxygen pressure (PaO2) might aggravate post-anoxic brain injury, clinical studies in patients resuscitated from cardiac arrest (CA) have given conflicting results. Some studies found that a PaO2 of more than 300 mm Hg (hyperoxemia) was an independent predictor of poor outcome, but others reported no association between blood oxygenation and neurological recovery in this setting. In this article, we review the potential mechanisms of oxygen toxicity after CA, animal data available in this field, and key human studies dealing with the impact of oxygen management in CA patients, highlighting some potential confounders and limitations and indicating future areas of research in this field. From the currently available literature, high oxygen concentrations during cardiopulmonary resuscitation seem preferable, whereas hyperoxemia should be avoided in the post-CA care. A specific threshold for oxygen toxicity has not yet been identified. The mechanisms of oxygen toxicity after CA, such as seizure development, reactive oxygen species production, and the development of organ dysfunction, need to be further evaluated in prospective studies.
Figures
Comment in
-
Hyperoxemia--too much of a good thing?Crit Care. 2014 Oct 7;18(5):556. doi: 10.1186/s13054-014-0556-3. Crit Care. 2014. PMID: 25673212 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lemiale V, Dumas F, Mongardon N, Giovanetti O, Charpentier J, Chiche JD, Carli P, Mira JP, Nolan J, Cariou A. Intensive care unit mortality after cardiac arrest: the relative contribution of shock and brain injury in a large cohort. Intensive Care Med. 2013;39:1972–1980. doi: 10.1007/s00134-013-3043-4. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical