Systems pharmacology dissection of the anti-inflammatory mechanism for the medicinal herb Folium eriobotryae
- PMID: 25636035
- PMCID: PMC4346873
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms16022913
Systems pharmacology dissection of the anti-inflammatory mechanism for the medicinal herb Folium eriobotryae
Abstract
Inflammation is a hallmark of many diseases like diabetes, cancers, atherosclerosis and arthritis. Thus, lots of concerns have been raised toward developing novel anti-inflammatory agents. Many alternative herbal medicines possess excellent anti-inflammatory properties, yet their precise mechanisms of action are yet to be elucidated. Here, a novel systems pharmacology approach based on a large number of chemical, biological and pharmacological data was developed and exemplified by a probe herb Folium Eriobotryae, a widely used clinical anti-inflammatory botanic drug. The results show that 11 ingredients of this herb with favorable pharmacokinetic properties are predicted as active compounds for anti-inflammatory treatment. In addition, via systematic network analyses, their targets are identified to be 43 inflammation-associated proteins including especially COX2, ALOX5, PPARG, TNF and RELA that are mainly involved in the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) signaling pathway, the rheumatoid arthritis pathway and NF-κB signaling pathway. All these demonstrate that the integrated systems pharmacology method provides not only an effective tool to illustrate the anti-inflammatory mechanisms of herbs, but also a new systems-based approach for drug discovery from, but not limited to, herbs, especially when combined with further experimental validations.
Figures
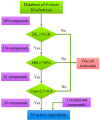

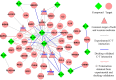
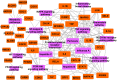
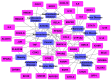
References
-
- Martinez Gonzalez J., Badimon L. Mechanisms underlying the cardiovascular effects of COX-inhibition: Benefits and risks. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2007;13:2215–2227. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

