Chinese herbal medicine for resistant hypertension: a systematic review
- PMID: 25636788
- PMCID: PMC4316421
- DOI: 10.1136/bmjopen-2014-005355
Chinese herbal medicine for resistant hypertension: a systematic review
Abstract
Objectives: This study aimed to summarise the current evidence from randomised control trials (RCTs) concerning treatment of patients with resistant hypertension with Chinese herbal medicine (CHM).
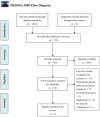
Design: Seven databases, including the Cochrane Library, PubMed, EMBASE, CNKI, VIP, CBM and Wanfang, were systematically searched from their inception to March 2014 for RCTs investigating treatment of resistant hypertension in which CHM was used either as a monotherapy or in combination with conventional medicine versus placebo, no intervention or conventional medicine.
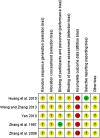
Results: Five trials containing 446 hypertensive patients were identified. The methodological quality of most trials was evaluated as generally low. All included trials compared CHM plus antihypertensive drugs with antihypertensive drugs alone for resistant hypertension. Formulations of CHM included tablet, decoction and injection. It was found that, compared with antihypertensive drugs alone, CHM (tablet) plus antihypertensive drugs resulted in clinically, but not statistically, significant reductions in systolic blood pressure (SBP; weighted mean difference (WMD)=-10.32 mm Hg; 95% CI -21.10 to 0.46; p=0.06) and diastolic blood pressure (DBP; WMD=-3.30 mm Hg; 95% CI -7.66 to 1.06; p=0.14). CHM (decoction) plus antihypertensive drugs also produced a clinically meaningful, but not statistically significant, reduction in SBP (WMD=-12.56 mm Hg; 95% CI -26.83 to 1.71; p=0.08), and did significantly decrease DBP (WMD=-7.89 mm Hg; 95% CI -11.74 to -4.04; p<0.0001). There were no significant differences in SBP (WMD=-3.50 mm Hg; 95% CI -8.95 to 1.95; p=0.21) and DBP (WMD=1.00 mm Hg; 95% CI -1.39 to 3.39; p=0.41) between CHM (injection) plus the antihypertensive drugs group and antihypertensive drugs alone. The safety of CHM remained uncertain.
Conclusions: No definite conclusions about the effectiveness and safety of CHM for resistant hypertension could be drawn. More rigorously designed trials are warranted.
Keywords: Chinese herbal medicine; resistant hypertension; systematic review.
Published by the BMJ Publishing Group Limited. For permission to use (where not already granted under a licence) please go to http://group.bmj.com/group/rights-licensing/permissions.
Figures
References
-
- Mancia G, Fagard R, Narkiewicz K et al. 2013 ESH/ESC guidelines for the management of arterial hypertension: the task force for the management of arterial hypertension of the European Society of Hypertension (ESH) and of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). Eur Heart J 2013;34:2159–219. 10.1093/eurheartj/eht151 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Calhoun DA, Jones D, Textor S et al. Resistant hypertension: diagnosis, evaluation, and treatment: a scientific statement from the American Heart Association Professional Education Committee of the Council for High Blood Pressure Research. Circulation 2008;117:510–26. 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.108.189141 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical