Phosphorylated α-synuclein in Parkinson's disease: correlation depends on disease severity
- PMID: 25637461
- PMCID: PMC4362824
- DOI: 10.1186/s40478-015-0185-3
Phosphorylated α-synuclein in Parkinson's disease: correlation depends on disease severity
Abstract
Introduction: α-Synuclein (α-syn) is a key protein in Parkinson's disease (PD), and one of its phosphorylated forms, pS129, is higher in PD patients than healthy controls. However, few studies have examined its levels in longitudinally collected cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) or in preclinical cases. In this study, CSF and clinical data were contributed by >300 subjects from three cohorts (the longitudinal DATATOP cohort, a large cross-sectional cohort, and a cohort of LRRK2 mutation carriers).
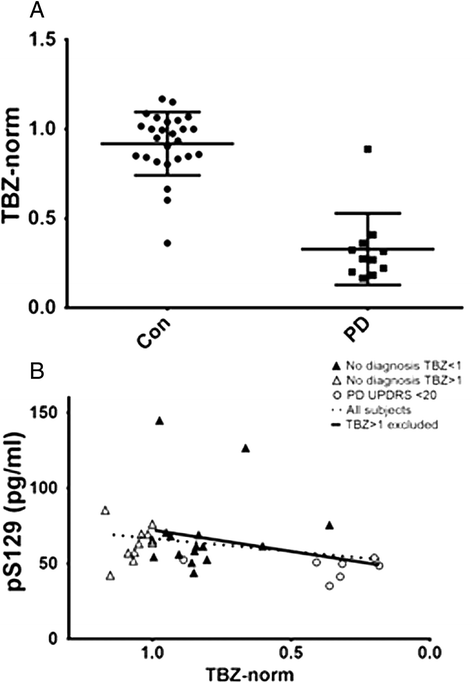
Results: Consistent with our previous observation that CSF pS129 positively correlated with Unified Parkinson's Disease Rating Scale (UPDRS) scores, CSF pS129 in the DATATOP cohort increased over approximately two years of disease progression (mean change 5.60 pg/ml, p = 0.050). Intriguingly, in the DATATOP cohort, pS129 negatively correlated with UPDRS scores at the baseline (R = -0.244, p = 0.017), but not final point, suggesting that this association may depend on disease stage. Reanalysis of our previous cohort with stratification by PD stage, and addition of a cohort of LRRK2 mutation carriers with very early/preclinical PD, supported the idea that the relationship between CSF pS129 and disease severity over a wider range of PD stages might be represented with a U-shaped curve, in which lower pS129 levels correlated with worse clinical condition at early stages, but better condition at later stages.
Conclusion: The observation of a negative-to-positive transition of correlation of pS129 to disease severity as PD progresses could have profound impact on how pS129 is used as a biomarker clinically as well as in modeling PD experimentally.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 NS057567/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P42 ES004696-5897/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS065070/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- T32 ES015459/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 ES019277/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 ES016873/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- T32 ES007032/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- P50 NS072187/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P50 NS062684/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P50 NS062684-6221/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG033398/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 ES007033-6364/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 NS082137/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

