Pulmonary epithelial barrier function: some new players and mechanisms
- PMID: 25637609
- PMCID: PMC4747906
- DOI: 10.1152/ajplung.00309.2014
Pulmonary epithelial barrier function: some new players and mechanisms
Abstract
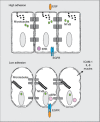
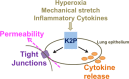
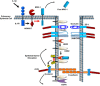
The pulmonary epithelium serves as a barrier to prevent access of the inspired luminal contents to the subepithelium. In addition, the epithelium dictates the initial responses of the lung to both infectious and noninfectious stimuli. One mechanism by which the epithelium does this is by coordinating transport of diffusible molecules across the epithelial barrier, both through the cell and between cells. In this review, we will discuss a few emerging paradigms of permeability changes through altered ion transport and paracellular regulation by which the epithelium gates its response to potentially detrimental luminal stimuli. This review is a summary of talks presented during a symposium in Experimental Biology geared toward novel and less recognized methods of epithelial barrier regulation. First, we will discuss mechanisms of dynamic regulation of cell-cell contacts in the context of repetitive exposure to inhaled infectious and noninfectious insults. In the second section, we will briefly discuss mechanisms of transcellular ion homeostasis specifically focused on the role of claudins and paracellular ion-channel regulation in chronic barrier dysfunction. In the next section, we will address transcellular ion transport and highlight the role of Trek-1 in epithelial responses to lung injury. In the final section, we will outline the role of epithelial growth receptor in barrier regulation in baseline, acute lung injury, and airway disease. We will then end with a summary of mechanisms of epithelial control as well as discuss emerging paradigms of the epithelium role in shifting between a structural element that maintains tight cell-cell adhesion to a cell that initiates and participates in immune responses.
Keywords: epithelial barrier; ions; lung; permeability; transport.
Copyright © 2015 the American Physiological Society.
Figures
References
-
- Ablimit A, Hasan B, Lu W, Qin W, Wushouer Q, Zhong N, Upur H. Changes in water channel aquaporin 1 and aquaporin 5 in the small airways and the alveoli in a rat asthma model. Micron 45: 68–73, 2013. - PubMed
-
- Adir Y, Welch LC, Dumasius V, Factor P, Sznajder JI, Ridge KM. Overexpression of the Na-K-ATPase α2-subunit improves lung liquid clearance during ventilation-induced lung injury. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 294: L1233–L1237, 2008. - PubMed
-
- Al-Bazzaz FJ, Hafez N, Tyagi S, Gailey CA, Toofanfard M, Alrefai WA, Nazir TM, Ramaswamy K, Dudeja PK. Detection of Cl-HCO3- and Na+-H+ exchangers in human airways epithelium. JOP 2: 285–290, 2001. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

