Deletion of Shank1 has minimal effects on the molecular composition and function of glutamatergic afferent postsynapses in the mouse inner ear
- PMID: 25637745
- PMCID: PMC4485438
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heares.2015.01.008
Deletion of Shank1 has minimal effects on the molecular composition and function of glutamatergic afferent postsynapses in the mouse inner ear
Abstract
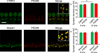
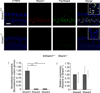
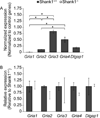
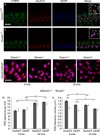
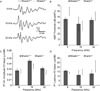
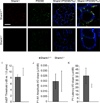
Shank proteins (1-3) are considered the master organizers of glutamatergic postsynaptic densities in the central nervous system, and the genetic deletion of either Shank1, 2, or 3 results in altered composition, form, and strength of glutamatergic postsynapses. To investigate the contribution of Shank proteins to glutamatergic afferent synapses of the inner ear and especially cochlea, we used immunofluorescence and quantitative real time PCR to determine the expression of Shank1, 2, and 3 in the cochlea. Because we found evidence for expression of Shank1 but not 2 and 3, we investigated the morphology, composition, and function of afferent postsynaptic densities from defined tonotopic regions in the cochlea of Shank1(-/-) mice. Using immunofluorescence, we identified subtle changes in the morphology and composition (but not number and localization) of cochlear afferent postsynaptic densities at the lower frequency region (8 kHz) in Shank1(-/-) mice compared to Shank1(+/+) littermates. However, we detected no differences in auditory brainstem responses at matching or higher frequencies. We also identified Shank1 in the vestibular afferent postsynaptic densities, but detected no differences in vestibular sensory evoked potentials in Shank1(-/-) mice compared to Shank1(+/+) littermates. This work suggests that Shank proteins play a different role in the development and maintenance of glutamatergic afferent synapses in the inner ear compared to the central nervous system.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Boeckers TM, Winter C, Smalla KH, Kreutz MR, Bockmann J, Seidenbecher C, Garner CC, Gundelfinger ED. Proline-rich synapse-associated proteins ProSAP1 and ProSAP2 interact with synaptic proteins of the SAPAP/GKAP family. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1999;264:247–252. - PubMed
-
- Boeckers TM, Segger-Junius M, Iglauer P, Bockmann J, Gundelfinger ED, Kreutz MR, Richter D, Kindler S, Kreienkamp HJ. Differential expression and dendritic transcript localization of Shank family members: identification of a dendritic targeting element in the 3’ untranslated region of Shank1 mRNA. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2004;26:182–190. - PubMed
-
- Burkard R, Feldman M, Voigt HF. Brainstem auditory-evoked response in the rat. Normative studies, with observations concerning the effects of ossicular disruption. Audiology. 1990;29:146–162. - PubMed
-
- Chen Z, Kujawa SG, Sewell WF. Auditory sensitivity regulation via rapid changes in expression of surface AMPA receptors. Nat Neurosci. 2007;10:1238–1240. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

