Alternative arrangements of telomeric recognition sites regulate the binding mode of the DNA-binding domain of yeast Rap1
- PMID: 25637888
- PMCID: PMC4459892
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bpc.2015.01.002
Alternative arrangements of telomeric recognition sites regulate the binding mode of the DNA-binding domain of yeast Rap1
Abstract
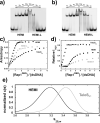
The function of yeast Rap1 as an activator in transcription, a repressor at silencer elements, and as a major component of the shelterin-like complex at telomeres requires the known high-affinity and specific interaction of the DNA-binding domain (DBD) with its recognition sequences. In addition to a high-affinity one-to-one complex with its DNA recognition site, Rap1(DBD) also forms lower affinity complexes with higher stoichiometries on DNA. We proposed that this originates from the ability of Rap1(DBD) to access at least two DNA-binding modes. In this work, we show that Rap1(DBD) binds in multiple binding modes to recognition sequences that contain different spacer lengths between the hemi-sites. We also provide evidence that in the singly-ligated complex Rap1(DBD) binds quite differently to these sequences. Rap1(DBD) also binds to a single half-site but does so using the alternative DNA-binding mode where only a single Myb-like domain interacts with DNA. We found that all arrangements of Rap1 sites tested are represented within the telomeric sequence and our data suggest that at telomeres Rap1 might form a nucleoprotein complex with a heterogeneous distribution of bound states.
Keywords: Analytical ultracentrifugation; Fluorescence anisotropy; Protein–DNA interaction; Telomeres.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures



Similar articles
-
The DNA-binding domain of yeast Rap1 interacts with double-stranded DNA in multiple binding modes.Biochemistry. 2014 Dec 9;53(48):7471-83. doi: 10.1021/bi501049b. Epub 2014 Nov 21. Biochemistry. 2014. PMID: 25382181 Free PMC article.
-
The wrapping loop and Rap1 C-terminal (RCT) domain of yeast Rap1 modulate access to different DNA binding modes.J Biol Chem. 2015 May 1;290(18):11455-66. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M115.637678. Epub 2015 Mar 24. J Biol Chem. 2015. PMID: 25805496 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of the yeast telomere nucleoprotein core: Rap1 binds independently to each recognition site.J Biol Chem. 2010 Nov 12;285(46):35814-24. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.170167. Epub 2010 Sep 7. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20826803 Free PMC article.
-
The different (sur)faces of Rap1p.Mol Genet Genomics. 2003 Mar;268(6):791-8. doi: 10.1007/s00438-002-0801-3. Epub 2003 Jan 25. Mol Genet Genomics. 2003. PMID: 12655405 Review.
-
The multifunctional transcription factor Rap1: a regulator of yeast physiology.Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2016 Jun 1;21(5):918-30. doi: 10.2741/4429. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2016. PMID: 27100480 Review.
Cited by
-
Nascent RNA signaling to yeast RNA Pol II during transcription elongation.PLoS One. 2018 Mar 23;13(3):e0194438. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0194438. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 29570714 Free PMC article.
-
The mitochondrial single-stranded DNA binding protein from S. cerevisiae, Rim1, does not form stable homo-tetramers and binds DNA as a dimer of dimers.Nucleic Acids Res. 2018 Aug 21;46(14):7193-7205. doi: 10.1093/nar/gky530. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018. PMID: 29931186 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kurtz S, Shore D. RAP1 protein activates and silences transcription of mating-type genes in yeast. Genes Dev. 1991;5:616–628. - PubMed
-
- Lustig AJ, Kurtz S, Shore D. Involvement of the Silencer and Uas Binding-Protein Rap1 in Regulation of Telomere Length. Science. 1990;250:549–553. - PubMed
-
- Kyrion G, Liu K, Liu C, Lustig AJ, Lustig AJ. Rap1 and Telomere Structure Regulate Telomere Position Effects in Saccharomyces-Cerevisiae. Genes & Development. 1993;7:1146–1159. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

