Development and Pilot Testing of Daily Interactive Voice Response (IVR) Calls to Support Antiretroviral Adherence in India: A Mixed-Methods Pilot Study
- PMID: 25638037
- PMCID: PMC4498985
- DOI: 10.1007/s10461-014-0983-9
Development and Pilot Testing of Daily Interactive Voice Response (IVR) Calls to Support Antiretroviral Adherence in India: A Mixed-Methods Pilot Study
Abstract
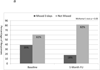
This two-phase pilot study aimed to design, pilot, and refine an automated interactive voice response (IVR) intervention to support antiretroviral adherence for people living with HIV (PLH), in Kolkata, India. Mixed-methods formative research included a community advisory board for IVR message development, 1-month pre-post pilot, post-pilot focus groups, and further message development. Two IVR calls are made daily, timed to patients' dosing schedules, with brief messages (<1-min) on strategies for self-management of three domains: medical (adherence, symptoms, co-infections), mental health (social support, stress, positive cognitions), and nutrition and hygiene (per PLH preferences). Three ART appointment reminders are also sent each month. One-month pilot results (n = 46, 80 % women, 60 % sex workers) found significant increases in self-reported ART adherence, both within past three days (p = 0.05) and time since missed last dose (p = 0.015). Depression was common. Messaging content and assessment domains were expanded for testing in a randomized trial currently underway.
Figures
References
-
- Agyapong VIO, Ahern S, McLoughlin DM, Farren CK. Supportive text messaging for depression and comorbid alcohol use disorder: Single-blind randomised trial. Journal of Affective Disorders. 2012;141:168–176. - PubMed
-
- Bangsberg DR. Less than 95% adherence to nonnucleoside reverse-transcriptase inhibitor therapy can lead to viral suppression. Clinical Infectious Diseases. 2006;43(7):939–941. - PubMed
-
- Bush K, Kivlahan DR, McDonell MB, Fihn SD, Bradley KA. The AUDIT alcohol consumption questions (AUDIT-C): an effective brief screening test for problem drinking. Archives of internal medicine. 1998;158(16):1789–1795. sd. - PubMed
-
- Chesney MA, Ickovics JR, Chambers DB, Gifford AL, Neidig J, Zwickl B, Wu AW. Self-reported adherence to antiretroviral medications among participants in HIV clinical trials: the AACTG adherence instruments. Patient Care Committee & Adherence Working Group of the Outcomes Committee of the Adult AIDS Clinical Trials Group (AACTG) AIDS Care. 2000;12(3):255–266. - PubMed
-
- Coomes CM, Lewis MA, Uhrig JD, Furberg RD, Harris JL, Bann CM. Beyond reminders: a conceptual framework for using short message service to promote prevention and improve healthcare quality and clinical outcomes for people living with HIV. AIDS Care. 2012;24(3):348–357. Epub 2011 Sep 21. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous