The use of stereotactic radiosurgery for brain metastases from breast cancer: who benefits most?
- PMID: 25638395
- PMCID: PMC4494730
- DOI: 10.1007/s10549-014-3242-x
The use of stereotactic radiosurgery for brain metastases from breast cancer: who benefits most?
Abstract
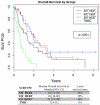
Brain metastases (BM) from primary breast cancer can arise despite use of systemic therapies that provide excellent extracranial disease control. Local modalities for treating BM include surgery, whole brain radiation therapy (WBRT), and stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS). We sought to determine the benefits of SRS for management of BM arising from different biologic breast cancer subtypes. We reviewed records of 131 patients who received SRS for breast cancer BM between 2001 and 2013. Survival was estimated by the Kaplan-Meier method. Effects of tumor biology, number and location of lesions, and number of SRS sessions on survival were evaluated by Cox proportional hazards regression. Of the 122 patients with subtypes available, 41 patients (31%) were classified as estrogen receptor positive/HER2 negative (ER(+)HER2(-)); 30 patients (23%), ER(+)HER2(+); 23 patients (18%), ER(-)HER2(+); and 28 patients (21%), ER(-)HER2(-) (or triple negative breast cancer, TNBC). Median age at first SRS was 50 years. Median overall survival for ER(+)HER2(-), ER(+)HER2(+), ER(-)HER2(+), and TNBC was 16, 26, 23, and 7 months, respectively (p < 0.001 for difference between groups). Patients with TNBC had the shortest time to retreatment with WBRT or SRS or death with hazard ratio of 3.12 (p < 0.001) compared to ER(+)HER2(-). In all subtypes other than TNBC, SRS can provide meaningful control of BM even in the setting of multiple lesions and may be worth repeating for new lesions that develop metachronously. For patients with TNBC, prognosis is guarded following SRS, and there is an urgent need to develop more effective treatment strategies.
Figures
References
-
- Barnholtz-Sloan JS, Sloan AE, Davis FG, Vigneau FD, Lai P, Sawaya RE. Incidence proportions of brain metastases in patients diagnosed (1973–2001) in the metropolitan detroit cancer surveillance system. J Clin Oncol. 2004;22(14):2865–2872. doi:10.1200/JCO.2004.12.149. - PubMed
-
- Chang EL, Wefel JS, Hess KR, Allen PK, Lang FF, Kornguth DG, Arbuckle RB, Swint JM, Shiu AS, Maor MH, Meyers CA. Neurocognition in patients with brain metastases treated with radiosurgery or radiosurgery plus whole-brain irradiation: a randomised controlled trial. Lancet Oncol. 2009;10(11):1037–1044. doi:10.1016/S1470-2045(09)70263-3. - PubMed
-
- Kased N, Binder DK, McDermott MW, Nakamura JL, Huang K, Berger MS, Wara WM, Sneed PK. Gamma knife radiosurgery for brain metastases from primary breast cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2009;75(4):1132–1140. doi:10.1016/j.ijrobp.2008.12.031. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous