Impact of a dedicated infusion clinic for acute management of adults with sickle cell pain crisis
- PMID: 25639822
- PMCID: PMC4409504
- DOI: 10.1002/ajh.23961
Impact of a dedicated infusion clinic for acute management of adults with sickle cell pain crisis
Abstract
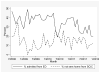
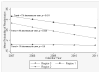
Most adults with sickle cell disease (SCD) receive care for their acute painful episodes in an emergency department (ED) setting. The purpose of this article is to describe the impact of opening a dedicated treatment center for adults with SCD [Sickle Cell Infusion Clinic (SCIC)] on patient outcomes and on hospital discharges for SCD. Descriptive data including demographics, time to first dose of narcotic, and pain scores were collected on patients presenting to the SCIC and ED. Maryland hospital discharge data were obtained from the Maryland Health Services Cost Review Commission. Analyses were conducted using T tests, χ(2) tests, and simple generalized estimating equation regression models accounting for the clustered nature of observations, as appropriate. There were 3,874 visits to the SCIC by 361 unique patients; 85% of those visits resulted in the patient being sent home. During the same time period, there were 3,408 visits to the ED by 558 unique patients with SCD. The overall admission rate from the ED for these patients was 35.9% but decreased significantly over the time period with a rate of 20% in December 2011. There was a significant decrease in readmissions over time for the entire Baltimore Metro area with the likelihood of readmission decreasing by 7% over time. The SCIC model provides adults with SCD access to high quality care that decreases the need for hospital admission. Further research needs to be done to evaluate the cost effectiveness of this model.
© 2015 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures

References
-
- Hassell KL. Population estimates of sickle cell disease in the U.S. Am J Prev Med. 2010;38:S512–S521. - PubMed
-
- Platt OS, Brambilla DJ, Rosse WF, et al. Mortality In Sickle Cell Disease -- Life Expectancy and Risk Factors for Early Death. N Engl J Med. 1994;330:1639–1644. - PubMed
-
- Haywood C, Jr, Beach MC, Lanzkron S, et al. A systematic review of barriers and interventions to improve appropriate use of therapies for sickle cell disease. J Natl Med Assoc. 2009;101:1022–1033. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
