Noninvasive fetal electrocardiography: an overview of the signal electrophysiological meaning, recording procedures, and processing techniques
- PMID: 25640061
- PMCID: PMC6931562
- DOI: 10.1111/anec.12259
Noninvasive fetal electrocardiography: an overview of the signal electrophysiological meaning, recording procedures, and processing techniques
Abstract
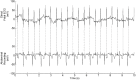
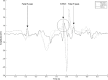
Background: Noninvasive fetal electrocardiography (fECG), obtained positioning electrodes on the maternal abdomen, is important in safeguarding the life and the health of the unborn child. This study aims to provide a review of the state of the art of fECG, and includes a description of the parameters useful for fetus clinical evaluation; of the fECG recording procedures; and of the techniques to extract the fECG signal from the abdominal recordings.
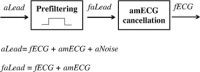
Methods: The fetus clinical status is inferred by analyzing growth parameters, supraventricular arrhythmias, ST-segment variability, and fetal-movement parameters from the fECG signal. This can be extracted from an abdominal recording obtained using one of the following two electrode-types configurations: pure-abdominal and mixed. Differently from the former, the latter also provides pure maternal ECG tracings. From a mathematical point of view, the abdominal recording is a summation of three signal components: the fECG signal (i.e., the signal of interest to be extracted), the abdominal maternal ECG (amECG), and the noise. Automatic extraction of fECG includes noise removal by abdominal signal prefiltration (0.5-45 Hz bandpass filter) and amECG cancellation.
Conclusions: Differences among methods rely on different techniques used to extract fECG. If pure abdominal electrode configurations are used, fECG is extracted directly from the abdominal recording using independent component analysis or template subtraction. Eventually, if mixed electrode configurations are used, the fECG can be extracted using the adaptive filtering fed with the maternal ECG recorded by the electrodes located in the woman thorax or shoulder.
Keywords: abdominal ECG; fetal monitoring; noninvasive fetal ECG.
© 2015 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Fetal Electrocardiogram Extraction and Analysis Using Adaptive Noise Cancellation and Wavelet Transformation Techniques.J Med Syst. 2017 Dec 8;42(1):21. doi: 10.1007/s10916-017-0868-3. J Med Syst. 2017. PMID: 29222728
-
Single-lead noninvasive fetal ECG extraction by means of combining clustering and principal components analysis.Med Biol Eng Comput. 2020 Feb;58(2):419-432. doi: 10.1007/s11517-019-02087-7. Epub 2019 Dec 19. Med Biol Eng Comput. 2020. PMID: 31858419
-
Morphology extraction of fetal ECG using temporal CNN-based nonlinear adaptive noise cancelling.PLoS One. 2022 Dec 15;17(12):e0278917. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0278917. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 36520789 Free PMC article.
-
A practical guide to non-invasive foetal electrocardiogram extraction and analysis.Physiol Meas. 2016 May;37(5):R1-R35. doi: 10.1088/0967-3334/37/5/R1. Epub 2016 Apr 12. Physiol Meas. 2016. PMID: 27067431 Review.
-
A Review of Signal Processing Techniques for Non-Invasive Fetal Electrocardiography.IEEE Rev Biomed Eng. 2020;13:51-73. doi: 10.1109/RBME.2019.2938061. Epub 2019 Aug 29. IEEE Rev Biomed Eng. 2020. PMID: 31478873 Review.
Cited by
-
Is Abdominal Fetal Electrocardiography an Alternative to Doppler Ultrasound for FHR Variability Evaluation?Front Physiol. 2017 May 16;8:305. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2017.00305. eCollection 2017. Front Physiol. 2017. PMID: 28559852 Free PMC article.
-
A systematic review of cardiac time intervals utilising non-invasive fetal electrocardiogram in normal fetuses.BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2018 Sep 12;18(1):370. doi: 10.1186/s12884-018-2006-8. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2018. PMID: 30208861 Free PMC article.
-
Dedicated Algorithm for Unobtrusive Fetal Heart Rate Monitoring Using Multiple Dry Electrodes.Sensors (Basel). 2021 Jun 23;21(13):4298. doi: 10.3390/s21134298. Sensors (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34201834 Free PMC article.
-
Automatic signal quality assessment of raw trans-abdominal biopotential recordings for non-invasive fetal electrocardiography.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2023 Feb 27;11:1059119. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2023.1059119. eCollection 2023. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2023. PMID: 36923461 Free PMC article.
-
Computerised Cardiotocography Analysis for the Automated Detection of Fetal Compromise during Labour: A Review.Bioengineering (Basel). 2023 Aug 25;10(9):1007. doi: 10.3390/bioengineering10091007. Bioengineering (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37760109 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Velayo C, Sato N, Ito T, et al. Understanding congenital heart defects through abdominal fetal electrocardiography: Case reports and clinical. J Obstet Gynaecol 2011;37:428–435. - PubMed
-
- Regitz‐Zagrosek V, Blomstrom‐Lundqvist C, Borghi C, et al. ESC guidelines on the management of cardiovascular diseases during pregnancy. The Task Force on the Management of Cardiovascular Diseases during Pregnancy of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). Eur Heart J 2001;32:3147–3197. - PubMed
-
- Steer PJ. Fetal distress. Curr Obstetr Gynaecol 2002;12:15–21.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

