The BDNF Val66Met polymorphism and plasma brain-derived neurotrophic factor levels in Han Chinese heroin-dependent patients
- PMID: 25640280
- PMCID: PMC4313085
- DOI: 10.1038/srep08148
The BDNF Val66Met polymorphism and plasma brain-derived neurotrophic factor levels in Han Chinese heroin-dependent patients
Abstract
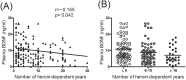
BDNF and its gene polymorphism may be important in synaptic plasticity and neuron survival, and may become a key target in the physiopathology of long-term heroin use. Thus, we investigated the relationships between brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) plasma concentrations and the BDNF Val66Met nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) in heroin-dependent patients. The pretreatment expression levels of plasma BDNF and the BDNF Val66Met SNP in 172 heroin-dependent patients and 102 healthy controls were checked. BDNF levels were significantly lower in patients (F = 52.28, p < 0.0001), but the distribution of the SNP was not significantly different. Nor were plasma BDNF levels significantly different between Met/Met, Met/Val, and Val/Val carriers in each group, which indicated that the BDNF Val66Met SNP did not affect plasma BDNF levels in our participants. In heroin-dependent patients, plasma BDNF levels were negatively correlated with the length of heroin dependency. Long-term (>15 years) users had significantly lower plasma BDNF levels than did short-term (<5 years) users. We conclude that plasma BDNF concentration in habitual heroin users are not affected by BDNF Val66Met gene variants, but by the length of the heroin dependency.
Figures
References
-
- Mintzer M. Z. & Stitzer M. L. Cognitive impairment in methadone maintenance patients. Drug Alcohol Depend 67, 41–51 (2002). - PubMed
-
- Thoenen H., Zafra F., Hengerer B. & Lindholm D. The synthesis of nerve growth factor and brain-derived neurotrophic factor in hippocampal and cortical neurons is regulated by specific transmitter systems. Ann N Y Acad Sci 640, 86–90 (1991). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

