Evaluation of a topical herbal patch for soft tissue wound healing: an animal study
- PMID: 25640329
- PMCID: PMC5024077
- DOI: 10.1111/jcpe.12372
Evaluation of a topical herbal patch for soft tissue wound healing: an animal study
Abstract
Aim: This study evaluated the effects of a topical herbal patch (PerioPatch®) for gingival wound healing in a rat model.
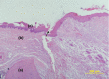
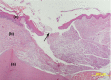
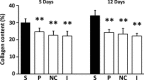
Materials and methods: A mid-crestal incision was performed on each side of the edentulous anterior maxilla in 48, 6-month-old, Wistar rats. Full-thickness flaps were raised, repositioned and sutured. Four experimental groups were established: herbal patch, placebo patch, no patch and no patch and no surgery. Patches were placed immediately after surgery and replaced every 12 h for the following 3 days. Half of the animals were killed after 5 and the remaining ones after 12 days. Tissue blocks were retrieved and processed for histological and immunohistochemical evaluation. Epithelial gap, collagen contents, amount of macrophages, cellular proliferation and vascular contents were evaluated in the central incision area. Statistical analysis consisted of two-way anova.
Results: The herbal patch group presented the smallest epithelial gap at 12 days, the highest collagen content both at 5 and 12 days, a larger number of proliferating cells at day 5 and more numerous blood vessels at day 12. Macrophage number was similar in all groups.
Conclusion: Herbal patch improved wound healing in this animal model.
Keywords: animal study; collagen; epithelium; herbal; histology; immunohistochemistry; inflammation; topical; wound healing.
© 2015 John Wiley & Sons A/S. Published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures




References
-
- Akbik, D. , Ghadiri, M. , Chrzanowski, W. & Rohanizadeh, R . (2014) Curcumin as a wound healing agent. Life Sciences 116, 11–7 - PubMed
-
- Belcaro, G. , Maquart, F. X. , Scoccianti, M. , Dugall, M. , Hosoi, M. , Cesarone, M. R. , Luzzi, R. , Cornelli, U. , Ledda, A. & Feragalli, B. (2011) TECA (Titrated Extract of Centella Asiatica): new microcirculatory, biomolecular, and vascular application in preventive and clinical medicine. A status paper. Panminerva Medica 53 (3 Suppl. 1), 105–118. - PubMed
-
- Carlson, E. R. & Monteleone, K. (2004) An analysis of inadvertent perforations of mucosa and skin concurrent with mandibular reconstruction. Journal of Oral Maxillofacial Surgery 62, 1103–1107. - PubMed
-
- Coldren, C. D. , Hashim, P. , Ali, J. M. , Oh, S. K. , Sinskey, A. J. & Rha, C. (2003) Gene expression changes in the human fibroblast induced by Centella asiatica triterpenoids. Planta Medica 69, 725–732. - PubMed
-
- Firat, C. , Samdanci, E. , Erbatur, S. , Aytekin, A. H. , Ak, M. , Turtay, M. G. & Coban, Y. K. (2013) β‐Glucan treatment prevents progressive burn ischaemia in the zone of stasis and improves burn healing: an experimental study in rats. Burns 39, 105–112. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

