Impaired uptake of conjugated bile acids and hepatitis b virus pres1-binding in na(+) -taurocholate cotransporting polypeptide knockout mice
- PMID: 25641256
- PMCID: PMC4657468
- DOI: 10.1002/hep.27694
Impaired uptake of conjugated bile acids and hepatitis b virus pres1-binding in na(+) -taurocholate cotransporting polypeptide knockout mice
Abstract
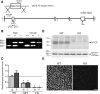
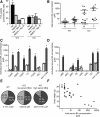
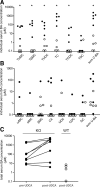
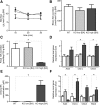
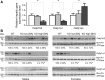
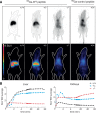
The Na(+) -taurocholate cotransporting polypeptide (NTCP) mediates uptake of conjugated bile acids (BAs) and is localized at the basolateral membrane of hepatocytes. It has recently been recognized as the receptor mediating hepatocyte-specific entry of hepatitis B virus and hepatitis delta virus. Myrcludex B, a peptide inhibitor of hepatitis B virus entry, is assumed to specifically target NTCP. Here, we investigated BA transport and Myrcludex B binding in the first Slc10a1-knockout mouse model (Slc10a1 encodes NTCP). Primary Slc10a1(-/-) hepatocytes showed absence of sodium-dependent taurocholic acid uptake, whereas sodium-independent taurocholic acid uptake was unchanged. In vivo, this was manifested as a decreased serum BA clearance in all knockout mice. In a subset of mice, NTCP deficiency resulted in markedly elevated total serum BA concentrations, mainly composed of conjugated BAs. The hypercholanemic phenotype was rapidly triggered by a diet supplemented with ursodeoxycholic acid. Biliary BA output remained intact, while fecal BA excretion was reduced in hypercholanemic Slc10a1(-/-) mice, explained by increased Asbt and Ostα/β expression. These mice further showed reduced Asbt expression in the kidney and increased renal BA excretion. Hepatic uptake of conjugated BAs was potentially affected by down-regulation of OATP1A1 and up-regulation of OATP1A4. Furthermore, sodium-dependent taurocholic acid uptake was inhibited by Myrcludex B in wild-type hepatocytes, while Slc10a1(-/-) hepatocytes were insensitive to Myrcludex B. Finally, positron emission tomography showed a complete abrogation of hepatic binding of labeled Myrcludex B in Slc10a1(-/-) mice.
Conclusion: The Slc10a1-knockout mouse model supports the central role of NTCP in hepatic uptake of conjugated BAs and hepatitis B virus preS1/Myrcludex B binding in vivo; the NTCP-independent hepatic BA uptake machinery maintains a (slower) enterohepatic circulation of BAs, although it is occasionally insufficient to clear BAs from the circulation.
© 2015 by the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases.
Figures

Comment in
-
The Na(+) -taurocholate cotransporting polypeptide knockout mouse: A new tool for study of bile acids and hepatitis B virus biology.Hepatology. 2015 Jul;62(1):19-21. doi: 10.1002/hep.27780. Epub 2015 Apr 8. Hepatology. 2015. PMID: 25761948 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Hofmann AF. Bile acids: the good, the bad, and the ugly. News Physiol Sci. 1999;14:24–29. - PubMed
-
- Meier PJ, Stieger B. Bile salt transporters. Annu Rev Physiol. 2002;64:635–661. - PubMed
-
- Stieger B. The role of the sodium-taurocholate cotransporting polypeptide (NTCP) and of the bile salt export pump (BSEP) in physiology and pathophysiology of bile formation. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2011;(201):205–259. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
