HCELL Expression on Murine MSC Licenses Pancreatotropism and Confers Durable Reversal of Autoimmune Diabetes in NOD Mice
- PMID: 25641589
- PMCID: PMC4447299
- DOI: 10.1002/stem.1948
HCELL Expression on Murine MSC Licenses Pancreatotropism and Confers Durable Reversal of Autoimmune Diabetes in NOD Mice
Abstract
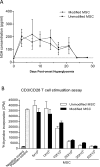
Type 1 diabetes (T1D) is an immune-mediated disease resulting in destruction of insulin-producing pancreatic beta cells. Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) possess potent immunomodulatory properties, garnering increasing attention as cellular therapy for T1D and other immunologic diseases. However, MSCs generally lack homing molecules, hindering their colonization at inflammatory sites following intravenous (IV) administration. Here, we analyzed whether enforced E-selectin ligand expression on murine MSCs could impact their effect in reversing hyperglycemia in nonobese diabetic (NOD) mice. Although murine MSCs natively do not express the E-selectin-binding determinant sialyl Lewis(x) (sLe(x) ), we found that fucosyltransferase-mediated α(1,3)-exofucosylation of murine MSCs resulted in sLe(x) display uniquely on cell surface CD44 thereby creating hematopoietic cell E-/L-selectin ligand (HCELL), the E-selectin-binding glycoform of CD44. Following IV infusion into diabetic NOD mice, allogeneic HCELL(+) MSCs showed threefold greater peri-islet infiltrates compared to buffer-treated (i.e., HCELL(-) ) MSCs, with distribution in proximity to E-selectin-expressing microvessels. Exofucosylation had no effect on MSC immunosuppressive capacity in in vitro assays; however, although engraftment was temporary for both HCELL(+) and HCELL(-) MSCs, administration of HCELL(+) MSCs resulted in durable reversal of hyperglycemia, whereas only transient reversal was observed following administration of HCELL(-) MSCs. Notably, exofucosylation of MSCs generated from CD44(-/-) mice induced prominent membrane expression of sLe(x) , but IV administration of these MSCs into hyperglycemic NOD mice showed no enhanced pancreatotropism or reversal of hyperglycemia. These findings provide evidence that glycan engineering to enforce HCELL expression boosts trafficking of infused MSCs to pancreatic islets of NOD mice and substantially improves their efficacy in reversing autoimmune diabetes. Stem Cells 2013;33:1523-1531.
Keywords: Diabetes; Glycan engineering; Glycosyltransferase programmed stereosubstitution; HCELL; Mesenchymal stem cell.
© 2015 AlphaMed Press.
Figures





References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

